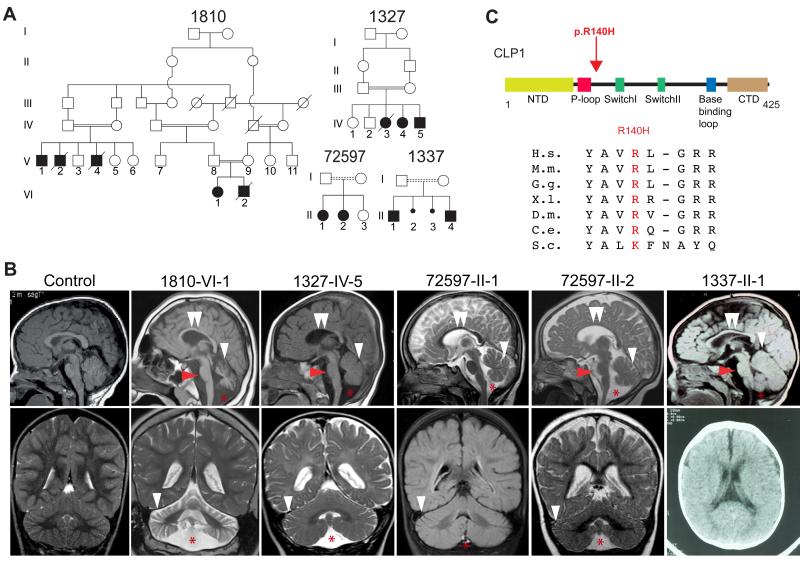
Figure 1.
Identification of a homozygous CLP1 p.R140H mutation in families with degeneration/hypoplasia of the central nervous system. Further analysis in Figure S1. (A) Pedigrees of four consanguineous Turkish families. Filled symbols: affecteds; hash: deceased; double bar: consanguinity; dashed double bar: history of consanguinity but ancestry not established. (B) Midline sagittal (top) and coronal (bottom) brain MRI of control compared with patients from each family, showing ventriculomegaly due to atrophy. Red arrowhead: hypoplastic/atrophic pons. White arrowhead: cerebellar folia atrophy. Double white arrowheads: hypoplastic corpus callosum. Red asterisk: Fluid cavity as a result of cerebellar atrophy (mega cisterna magna). Only axial CT was available for 1337-II-1. (C) Stick figure of CLP1 protein and location of the p.R140H mutation near the ATP-binding P-loop. Evolutionary conservation of the p.R140 residue across the animal kingdom. NTD: N-terminal domain; P-loop/Walker A motif; Switch loop I; Switch loop II; base-binding loop: involved in nucleotide binding; CTD: C-terminal domain. H.s.: Human; M.m.: Mouse; G.g.: Chicken; X.l.: Frog; D.m.: Fly; C.e.: Worm; S.c.: Yeast.