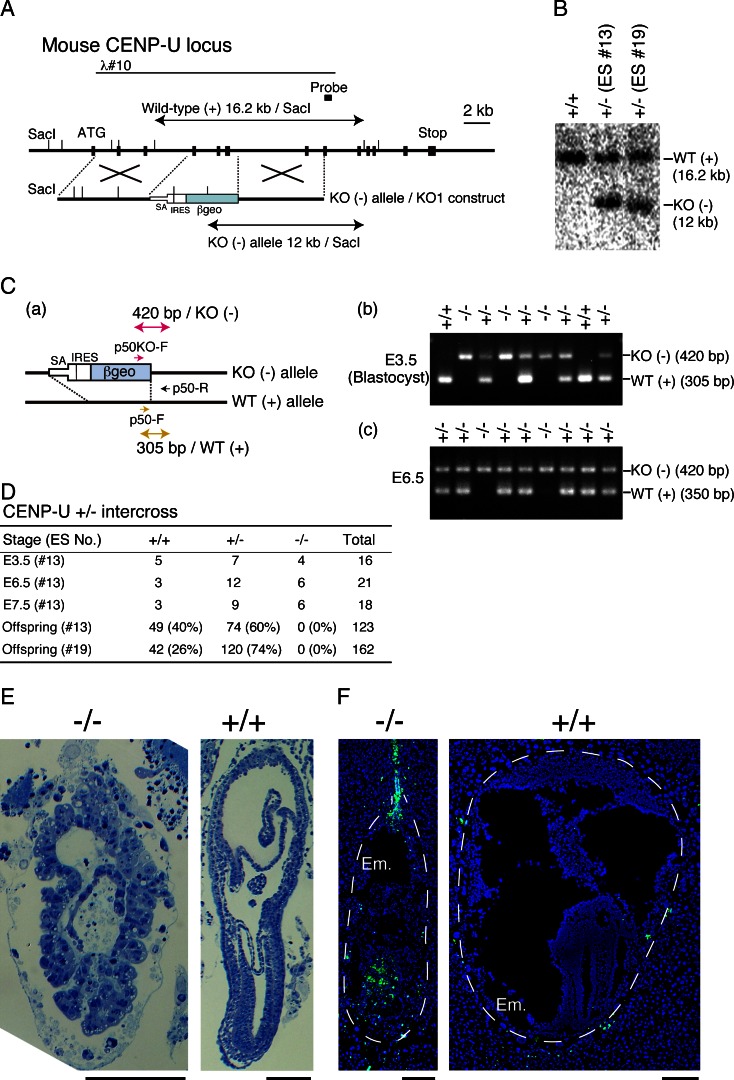
Fig. 1.
CENP-U is essential for mouse embryogenesis a Genomic region of the mouse CENP-U locus and a gene disruption construct. Black boxes indicate the positions of exons. Sac I restriction sites are shown. The position of the probe used for Southern hybridization is indicated. A novel 12-kb Sac I fragment hybridized to the probe, if targeted integration of the construct occurred. b Restriction analysis of genomic DNAs with targeted integration of the CENP-U disruption construct. Genomic DNAs from wild-type ES cells and two clones (#13 and #19) after targeting (+/−) were analyzed by Southern hybridization using the probe indicated in (A). In #13 and #19, a novel 12-kb Sac I fragment was detected. c PCR genotyping of embryonic DNA from mice of CENP-U+/− heterozygous intercrosses. a Primer design, b PCR results with DNA from E3.5, and c PCR results with DNA from E6.5. d Genotyping of CENP-U+/− intercross mice at each stage. e Serial section analysis of E7.5 embryos from wild-type or CENP-U−/− mice. Sections were stained with toluidine blue. Scale bar, 100 μm. f DAPI (blue) and TUNEL (green) staining of E7.5 embryos from the wild-type or CENP-U−/− mice. Scale bar, 200 μm. An embryo (Em.) is outlined by a dashed line. TUNEL positive cells are enriched in the −/− embryo