Table 2.
The comparison of the distribution of childhood maternal educational level and occupational status according to the MetS stratified by gender
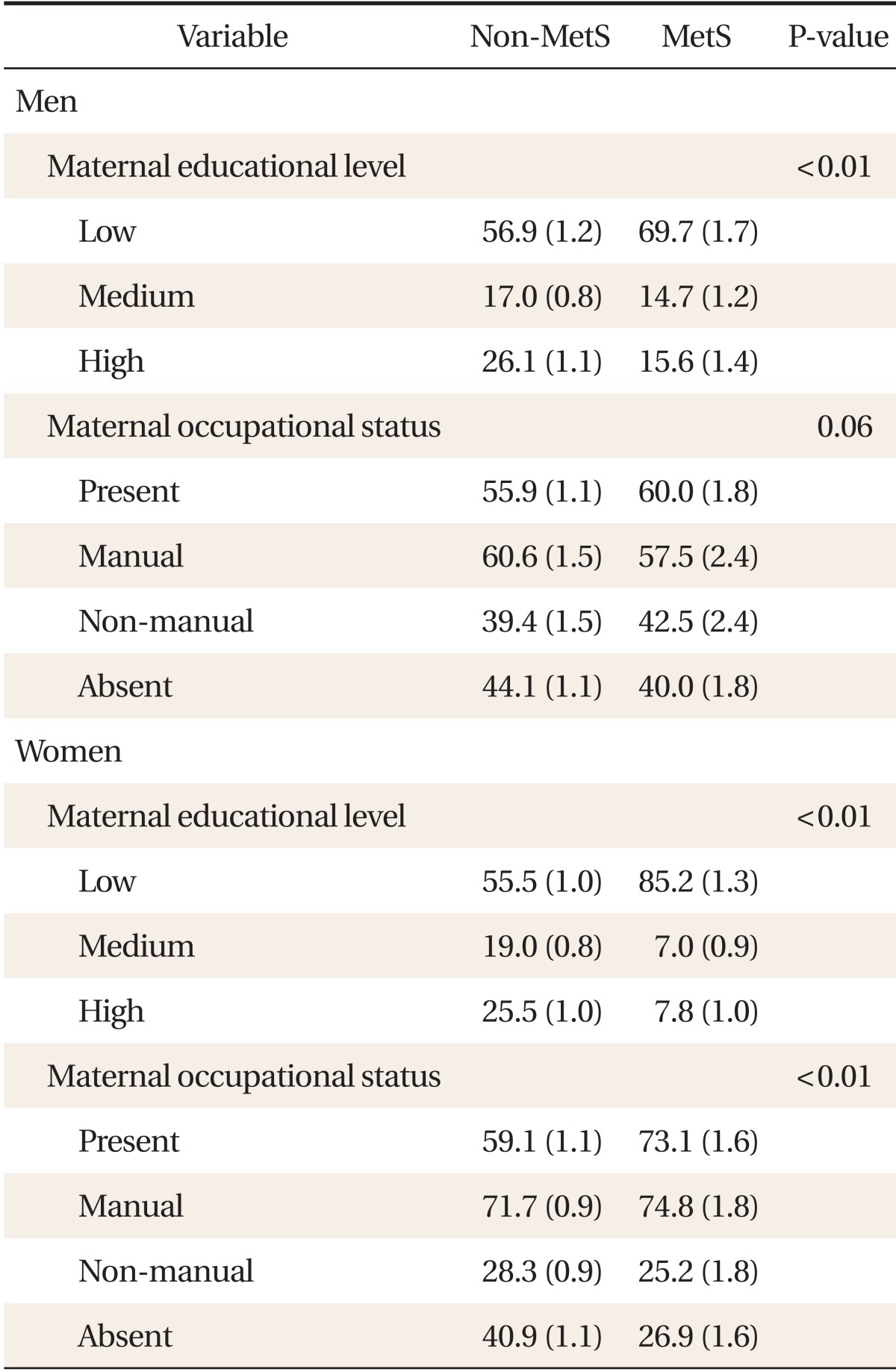
Values are presented as % (standard error). Metabolic syndrome (MetS) was defined as the presence of three or more of the following criteria: abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, high fasting glucose, high triglycerides levels, or low high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels. Abdominal obesity was defined as waist circumference ≥ 90 cm in males or ≥ 80 cm in females; high blood pressure was defined as systolic blood pressure ≥ 130 mm Hg, diastolic blood pressure ≥ 85 mm Hg, or a diagnosis of hypertension along with an anti-hypertensive drug regimen; high fasting glucose was defined as fasting plasma glucose levels ≥ 100 mg/dL, taking any drug for hyperglycemia, or using insulin for low blood sugar; high triglycerides (TGs) were defined as TG levels ≥ 150 mg/dL or taking any anti-dyslipidemic drug for hypertriglyceridemia; low HDL-C was defined as HDL-C levels < 40 mg/dL in males or < 50 mg/dL in females or taking any anti-dyslipidemic drugs for high HDL-C levels.
