Figure 2.
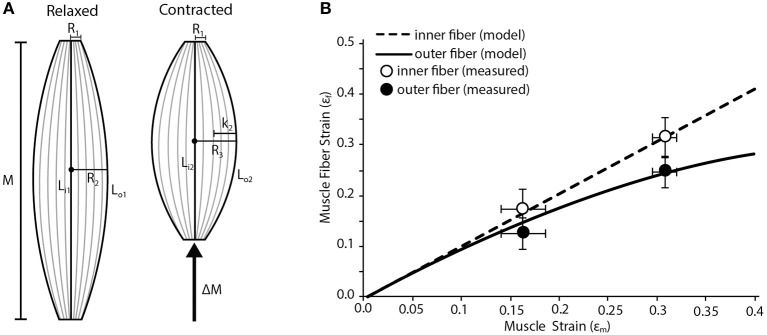
Fiber strain heterogeneity in a fusiform muscle. (A) Schematic of a fusiform muscle during relaxed and contracted conditions. Schematic is representative of a frog palmaris longus muscle. M denotes relaxed length of the muscle. LI1, the length of the inner fiber, is compared to Lo1, the length of the outer fiber. During contraction there is a change in muscle length (ΔM) along the line of action of the muscle. LI2, the length of the inner fiber after contraction, is compared to L02, the length of the outer fiber after contraction. The radius of the muscle increases (by length K2) from R2 to R3 during contraction. R1 is the radius of the muscle where it interacts with the tendon at both the origin and insertion and is assumed to remain constant during contraction. (B) The model predicts variation in the strain of the innermost and outermost muscle fibers as whole muscle strain increases. The inner fibers undergo relatively higher strains than the outer fibers. Closed and open circles represent empirically measured mean strain in the outermost and innermost fibers, respectively. Data are collected from the frog palmaris longus muscle (n = 4). Error bars represent the standard error of the mean.
