Table 1.
Summary of experimental results.
| KP | MM | Control subjects | Sight-recovery patients in previous studies | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Face perception | ||||
| Face/non-face discrimination | 23/26 No false positives |
21/26 Three false positives |
24/26 One false positive |
No errors (SRD) |
| Face localization | 7/10 images, or 39 out of a total of 42 faces localized | – | No errors | No errors (SRD) |
| Gender classification | 4/10 | 3/10 | No errors | 70% (MM); no errors (SRD) |
| Face discrimination | 12/30 | 15/30 | 26/30 | Inability to recognize faces reported (SB); inability to recognize faces reported (Virgil); 60% for 45° depth rotation (SRD) |
| Object recognition | ||||
| Canonical | 36/39 | – | – | 25% (MM; a combination of canonical and noncanonical viewpoints were used); 26% (SK); 34% (JA); 18% (PB) |
| Atypical color | 4/9 | 3/9 | 9/10 | – |
| Less-typical perspective | 6/10 | 4/10 | No errors | – |
| Silhouettes | 9/10 | 4/10 | No errors | – |
| Half-occluded | 9/10 | 0/10 | No errors | – |
| RISE | 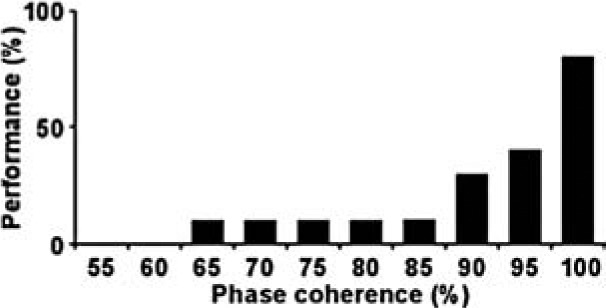 |
– | 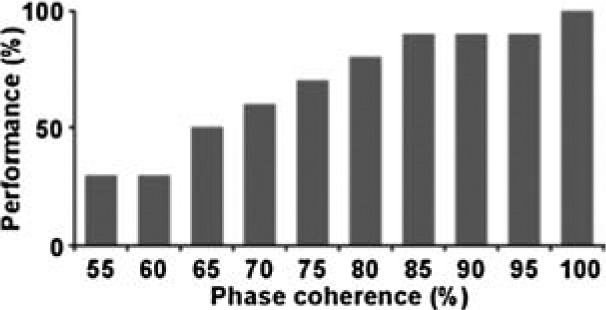 |
– |
| Visual space perception | ||||
| Depth cues | 6/8 Sensitivity to interposition, height in the visual field, and texture gradient; at least partial sensitivity to linear perspective |
– | No errors | Sensitivity to shadows and interposition, and insensitivity to perspective (MM); sensitivity to shadows, height in the visual field, and atmospheric perspective cues (SRD); partial sensitivity to interposition (SK) |
| Simple size constancy | In-depth stimuli perceived as smaller than frontal stimuli; more distant stimuli perceived as smaller than closer stimuli | – | – | – |
| Complex size constancy | Mean overestimation of 30%; interquartile range of 60%; low confidence about responses | – | Mean underestimation of 5%; interquartile range of 10% | Inability to estimate distances reported (SB); inability to estimate distances reported (HS, TG, ME, CA); inability to estimate distances reported (Virgil) |
| Visual illusions | Less susceptibility to context-induced visual illusions (Ponzo, Ebbinghaus, Sander, White) | – | Susceptibility to context-induced visual illusions | Less susceptibility to the Müller-Lyer, Poggendorff, Zöllner, and Hering illusions (SB); less susceptibility to Müller-Lyer (LG); susceptibility to simultaneous contrast, Müller-Lyer, and horizontal-vertical illusions (SRD) |
Note. HS, TG, ME, CA, LG (Valvo, 1971); SB (Gregory & Wallace, 1963); Virgil (Sacks, 1995); MM (Fine et al., 2003); SRD (Ostrovsky, Andalman, & Sinha, 2006); SK, JA, PB (Ostrovsky et al., 2009).
