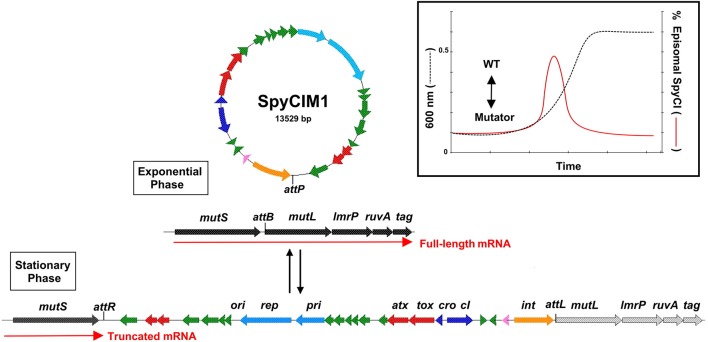
Figure 1.
SpyCIM1 regulates the MMR operon through dynamic site-specific excision and integration. The molecular switch controlled by SpyCIM1 is shown. The MMR operon of S. pyogenes is comprised of genes encoding DNA mismatch repair (mutS and mutL), multidrug efflux (lmrP), a Holliday-junction resolvase (ruvA), and base excision repair (tag). During exponential phase, SpyCIM1 excises from the chromosome, circularizes, and replicates as an episome, restoring transcription of the entire MMR operon (WT). Excision and mobilization occurs early in logarithmic growth in response to yet unknown cellular signals (Insert; adapted from Scott et al., 2008). As logarithmic growth continues, SpyCIM1 re-integrates into mutL at attB, and by the time the culture reaches stationary phase, the integration process has completed, again blocking transcription of the MMR operon. WT, Wild type phenotype associated with unimpeded expression of the MMR operon. Color key of predicted gene functions: Green, genes of unknown function; red, possible toxin-antitoxin maintenance genes; light blue, DNA replication; dark blue, control of lysogeny; pink, transmembrane peptide; orange, site-specific integrase.