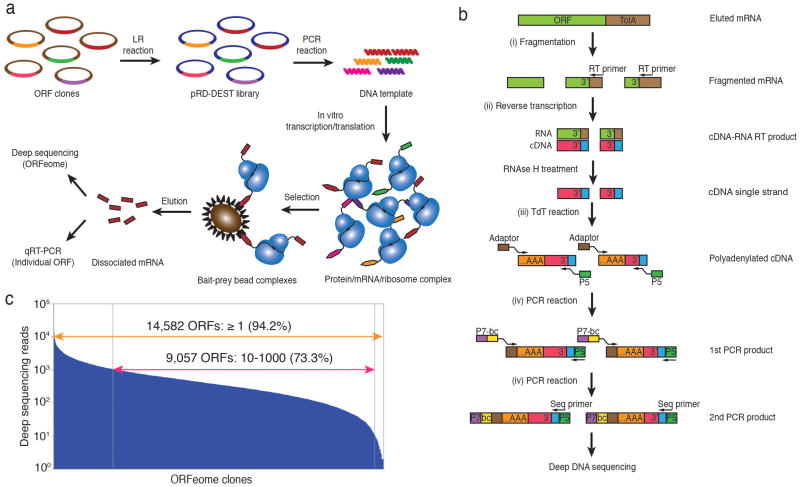
Figure 1.
Parallel analysis of in vitro translated ORFs (PLATO). (a) ORF display scheme. The pooled human ORFeome v5.1 entry vector library is is attL-attR (“LR”) recombined into the pRD-DEST expression vector. Expression plasmids are PCR amplified to generate the DNA templates for in vitro transcription. Following in vitro translation, the protein-mRNA-ribosome complexes are incubated with protein, antibody or small-molecule bait immobilized on beads. The enriched mRNA library is recovered from bait-prey bead complexes for further analysis. (b) Processing of mRNA samples for deep DNA sequencing. After fragmentation and reverse transcription (RT) using a universal primer to recover the 3′ end of ORFeome transcripts, cDNA is polyadenylated with terminal deoxynucleotide transferase (TdT) and amplified for multiplex deep sequencing using primers containing a sample barcode and the P5 and P7 Illumina sequencing adaptors. (c) Sequencing reads of the unenriched human pRD-ORFeome mRNA library (the ‘input’ library). Most ORFs were sequenced at least once.