Figure 1.
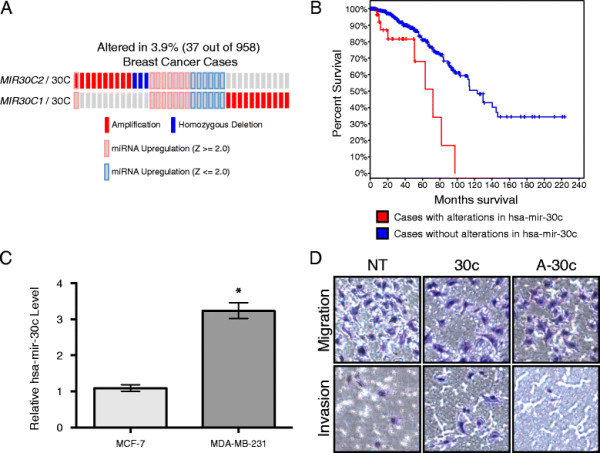
hsa-mir-30c promotes the invasiveness of MDA-MB-231 cells and regulates RUNX2 levels. (A) Oncoprint of breast cancer samples that have altered copy number in MIR30C1 or MIR30C2, or significantly differentially expressed levels of the mature miRNA, hsa-mir-30c. Differentially expressed samples are defined by having a Z score greater than 2.0 or less than −2.0. Z is calculated as the difference between the expression value of hsa-mir-30c and the mean expression value of hsa-mir-30c in samples that are diploid for MIR30C1/MIR30C2 divided by the standard deviation of the expression values for hsa-mir-30c in samples that are diploid for MIR30C1/MIR30C2. (B) Survival plot of patients with copy number alterations in MIR30C1/MIR30C2 or levels of hsa-mir-30c (red) versus patients with diploid MIR30C1/MIR30C2 or normal levels of hsa-mir-30c. Log-rank P-value < 1.09e-03. (C) Real Time qPCR detection of hsa-mir-30c in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells, normalized to U6 RNA. Mean and SEM (error bars) for two technical replicates of two biological replicates. * = Student’s t-test with Welch correction p-value < 0.05. (D) Representative Matrigel invasion assay using MDA-MB-231 cells following 48 h of transient transfection with non-targeting miRNA (NT), hsa-mir-30c (30c) or anti-hsa-mir-30c (A-30c); cells were stained with HEMA3.
