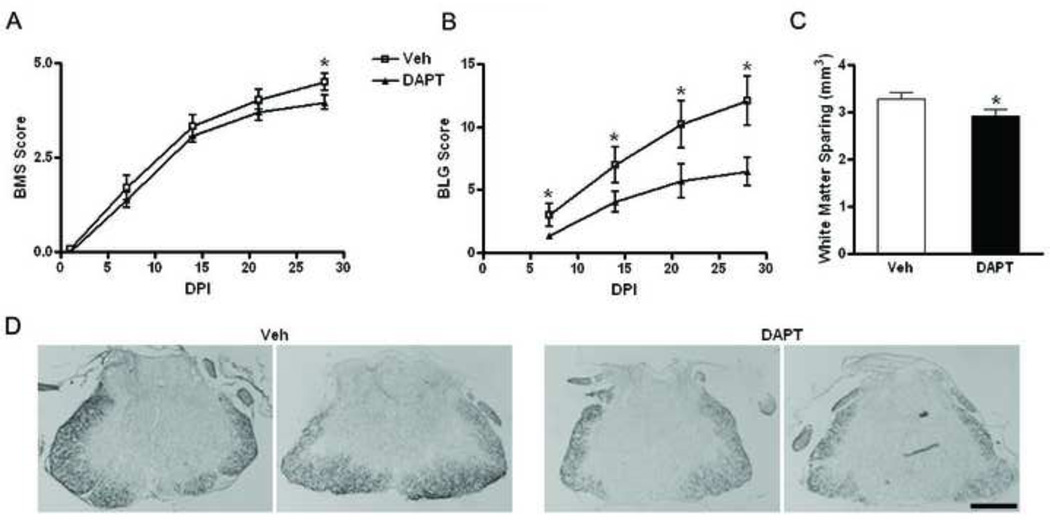
Figure 5. DAPT administration reduces the functional recovery after SCI in mice as measured by behavioral testing.
DAPT (30 mg/kg) and vehicle were administered orally twice a day for 10 days (n=12) starting 15 minutes after injury. Mice were evaluated using BMS and BLG scores at 1 day post-injury (DPI) and weekly thereafter. A. Vehicle-treated (Veh) mice have a significant (p value < 0.04) higher BMS score at 28 DPI. B. The mice were also evaluated based on their stepping using the BLG score. A significant improved performance of vehicle-treated mice is observed as early as 7 DPI. C. Sections from spinal cord (n=10) were processed for Eriochrome cyanine R staining and analyzed using sterological techniques. The white matter spared in the vehicle-treated is significantly (p value = 0.0384) higher than the DAPT-treated (DAPT) mice. D. Representative images show higher staining present in Veh as compared to DAPT mice at the epicenter (Mag. Bar = 500 µm).