Figure 2.
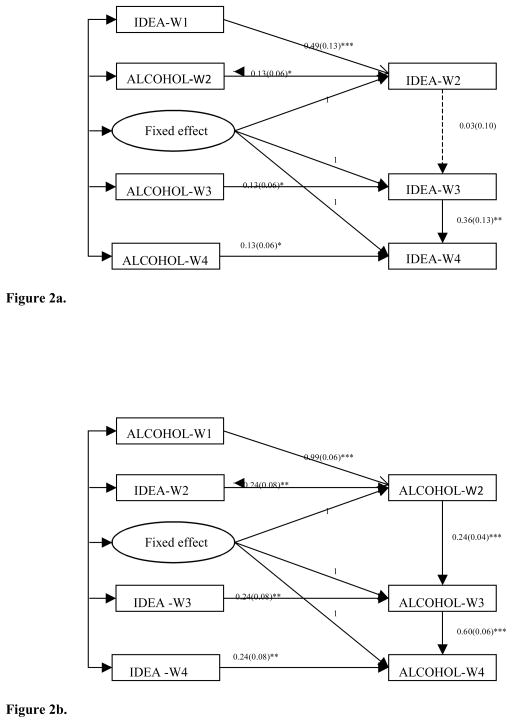
Figure 2a. Fixed effects model with lagged dependent variables-unidirectonal associaton from past-year alcohol use to suicidal ideaiton.
Note. * p<.05, ** p<.01, *** p<.001. All the covariances among exogenous variables were specified in the model, while not all of them were statistically sifnificant larger than 0. The covariances between fixed effect with past-year alcohol at each wave, and the covariances between suicidal ideation at wave 1 with past-year alcohol use at wave 3 and 4 were not sginificant. IDEA, Suicidal Ideation; ALCOHOL, Past-year Alcohol Use.
Figure 2b. Fixed effects model with lagged dependent variables-unidirectional association from suicidal ideation to past-year alcohol use.
Note. * p<.05, ** p<.01, *** p<.001. All the covariances among exogenous variables were specified in the model, while not all of them were statistically sifnificant larger than 0. The covariances between fixed effect with suicidal ideaiton at each wave, and the covariances between suicidal ideaiton at wave 3 with past-year alcohol use at wave 1 were not significant. IDEA, Suicidal Ideation; ALCOHOL, Past-year Alcohol Use.
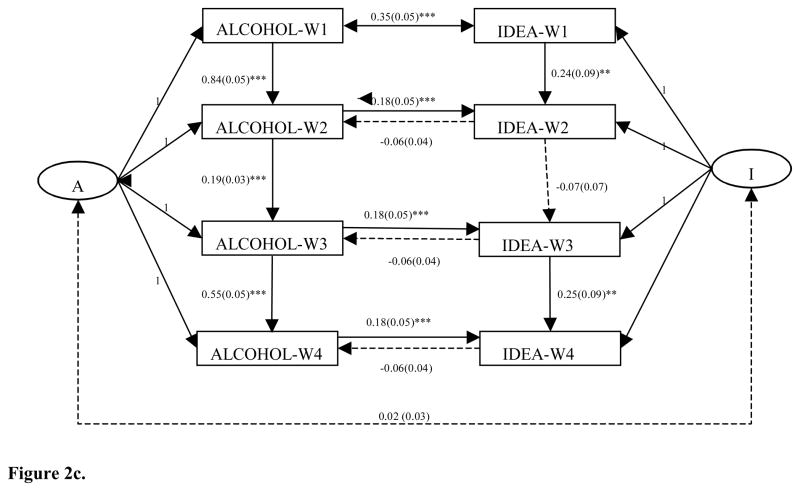
Figure 2c. A nonrecursive model: the reciprocal relations between past-year alcohol use and suicidal ideation.
Note. * p<.05, ** p<.01, *** p<.001. IDEA, Suicidal Ideation; Alcohol, Past-Year Alcohol Use; I, Fixed Effect of Suicial Ideation; A, Fixed Effect of Past-Year Alcohol Use.