Figure 4.
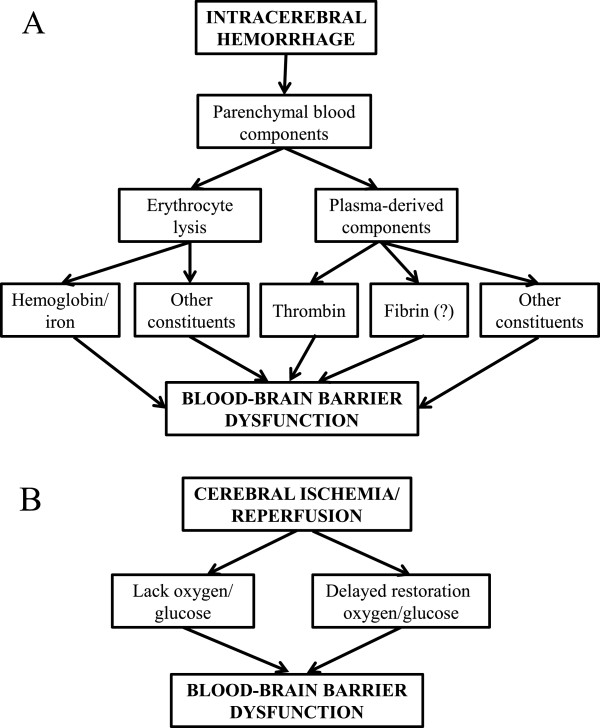
The underlying cause of secondary BBB dysfunction appears to differ in ICH (A) from cerebral ischemia (B). In ICH, evidence indicates a major role for the presence of blood components in brain parenchyma activating a number of pathways (cell injury, receptor-mediated signaling and inflammation) leading to BBB dysfunction. In contrast, in cerebral ischemia, the initiating cause of injury is the lack of oxygen and glucose supply to the brain. Delayed restoration of blood flow can also induce BBB dysfunction (reperfusion injury). With ischemic injury, there are a number of factors that can enhance the BBB dysfunction. Thus, for example, hyperglycemia and tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) both can result in hemorrhage after reperfusion. Less is known about factors that enhance secondary BBB dysfunction in ICH.
