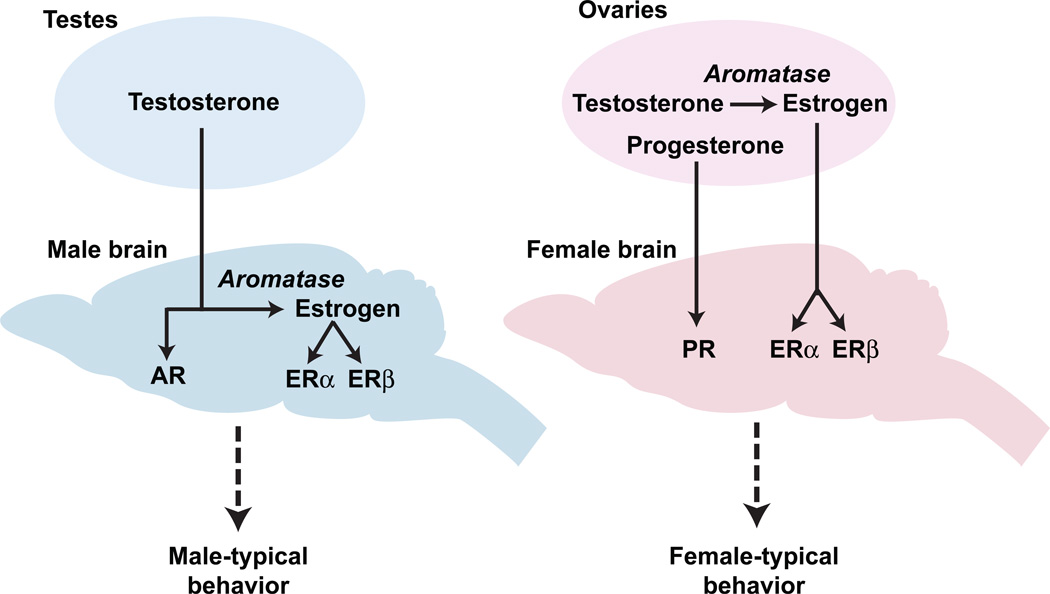
Figure 3. Sex hormone control of sexually dimorphic behaviors.
Sex hormones produced in the gonads cross the blood-brain barrier and bind to hormone receptors in neurons to regulate sex-typical behaviors. In males, testosterone directs behavior by binding to its receptor AR or it is converted via aromatase into estrogen, which binds to its cognate receptors ERα and ERβ. In females, estrogen and progesterone direct behavior via their cognate receptors ERα and ERβ and PR, respectively.