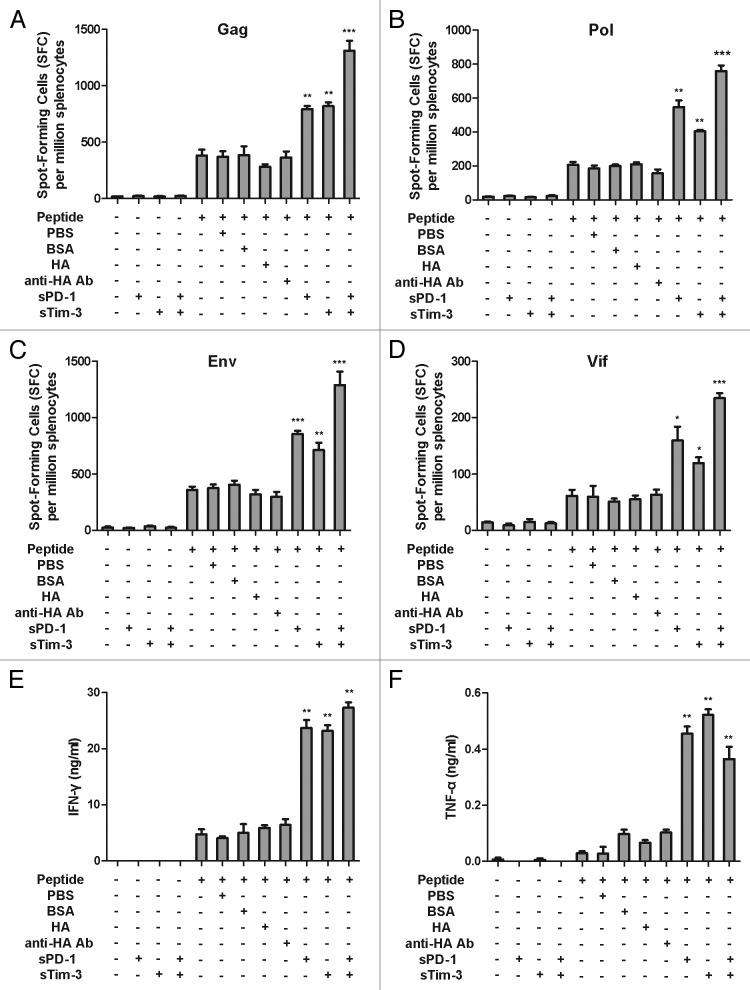
Figure 1. Effects of sPD-1 and sTim-3 on the frequency of IFN-γ spot-forming cells and secretion of IFN-γ and TNF-α of splenocytes from immunized mice ex vivo. (A, B, C, and D). Enhancement of Gag, Pol, Env, and Vif antigen specific IFN-γ spot-forming cells by sPD-1 and sTim-3. Splenocytes were isolated from C57BL/6 mice immunized with the rAd5-SIV and cultured with SIV Gag, Pol, Env, and Vif peptide pools respectively in the presence or absence of sPD-1 or sTim-3, or both sPD-1 and sTim-3. Twenty-four hours later, splenocytes were harvested and subjected to an IFN-γ ELISPOT assay. (E and F). Enhancement of IFN-γ and TNF-α secretion by sPD-1 and sTim-3. Splenocytes were stimulated with SIV peptides in the presence or absence of sPD-1 or sTim-3, or both sPD-1 and sTim-3. Twenty-four hours later, the culture media were measured for the secretion of IFN-γ and TNF-α using ELISA assays. BSA (bovine serum albumin), HA (influenza virus hemagglutinin), and anti-HA Ab (an anti-HA monoclonal antibody) were used as non-related protein controls (the concentration of BSA, HA, and anti-HA Ab in culture media was 16μg/ml). PBS (phosphate-buffered saline) was used as a background control. The data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA. The bars represent the standard errors. *P < 0.05;**P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. The figure is the representation of the data obtained from two independent experiments.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.