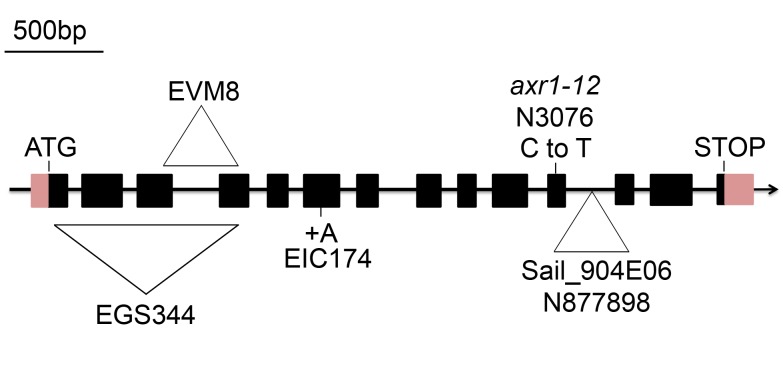
Figure 1. The AXR1 gene and axr1 mutations.
The arrow indicates the orientation of the open reading frame. Exons are shown as boxes (pink, UTR; black, CDS). In the EGS344 mutant, a large deletion associated with an insertion of the exogenous Agrobaterium Ti plasmid disrupts the AXR1 gene from nucleotide 91 (40 bp 5′ to the ATG). In the EVM8 mutant, an in-frame deletion of 312 bp between exons 3 and 4 generates a 20 aa truncated protein. In EIC174, a single nucleotide insertion (A) in exon 6 (position 1364 of the genomic sequence, corresponding to nt 688 in the cDNA) leads to a premature stop codon (a 222 aa protein is produced instead of the 540 aa protein in wild type). In axr1-12, corresponding to the N3076 line, a single C-T nucleotide substitution at position 1295 of the cDNA leads to a premature stop codon (415 aa instead of 540), as described by Leyser et al. [44]. In N877898, corresponding to the Sail_904E06 line, a T-DNA insertion occurred in intron 11. References used for this figure are Tair accession 4010763662 for the genomic sequence and Tair accession 4010730885 for the cDNA sequence.