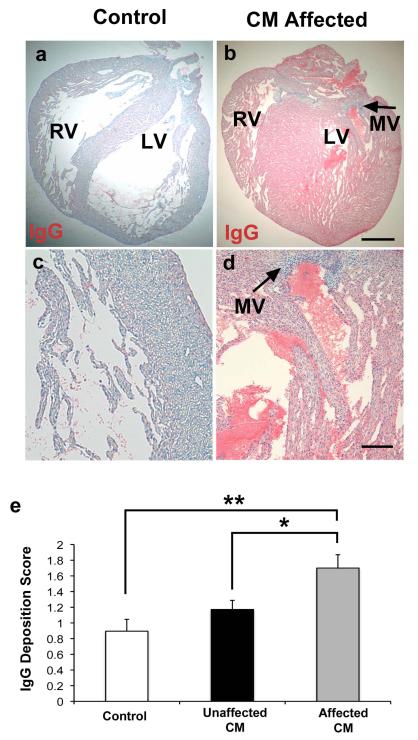
Figure 5. Increased immunoglobulin (IgG) deposition in myocardium of affected hearts.
Both affected and unaffected hearts were observed in the CM immunized group (32% of fetal rats developed HLHS-like phenotype). Anti-rat IgG alkaline phosphatase conjugated was used to detect IgG as indicated by Fast Red substrate against a counterstain of Mayer’s hematoxylin. (A and C) Adjuvant control hearts demonstrated minimal anti-rat IgG staining. (B and D) Affected hearts demonstrated extensive anti-rat IgG binding, indicated by increased Fast Red substrate staining. Left-sided mitral valve (MV) identified by arrows on affected heart. There is more IgG deposited within the myocardium of the affected hearts compared with valve structures. PBS treated control sections did not stain red and were blue and negative for IgG (not shown). (E) Scored results for amount of anti-rat IgG deposition. The affected group (n = 15) had increased IgG deposition compared to the unaffected group (n = 32 fetuses) (*P = 0.03) and adjuvant control (n = 19 fetuses) (**P = 0.002) groups. (A-B) 20x magnification. Scale bar, 600μm. (c-d) 100x magnification. Scale bar 125 μm. Three variables (E) analyzed using twoway analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey-Kramer adjustment for multiple comparisons. Average of data shown in bars are mean ± s.e.m.