Figure 2.
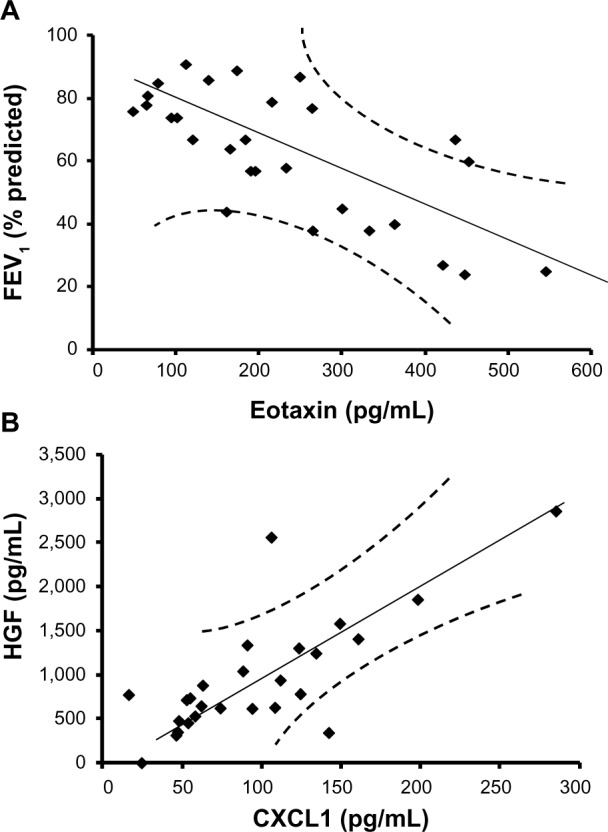
Increasing severity of airflow limitation is associated with decreasing levels of eotaxin, whereas chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 (CXCL1) is positively correlated with hepatocyte growth factor (HGF). (A) Eotaxin is negatively correlated with forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1; percentage predicted), as represented in the regression line. These data suggest that eotaxin is a good biomarker predicting FEV1 changes in stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. (B) The regression line for CXCL1 and hepatocyte growth factor shows a positive correlation, suggesting these two factors are dependent variables or regulated by the same transcription factor.
