Figure 2.
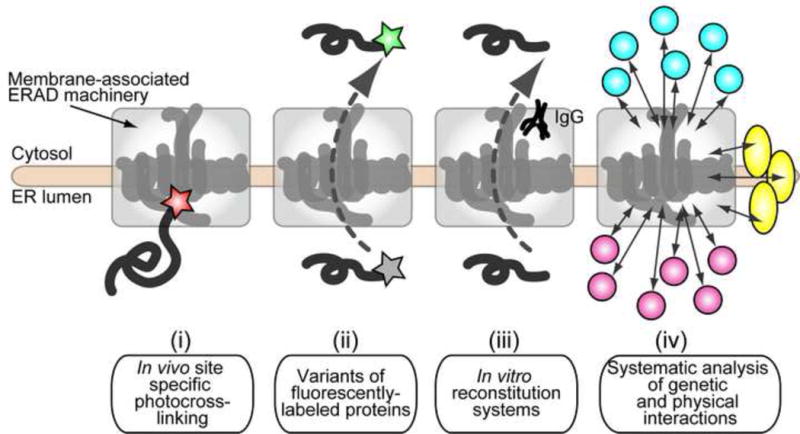
Select technologies that have improved our understanding of the ERAD pathway. (i) In vivo site specific photocross-linking revealed the direct interaction of substrates with components of the Hrd1 complex. (ii) Variants of fluorescent proteins were adopted to analyze retrotranslocation in vivo. (iii) Bottom-up reconstitutions that recapitulate each step during the ERAD pathway have elucidated the mechanisms that lead to substrate recognition, ubiquitylation, retrotranslocation, and degradation. (iv) Top-down and systematic genetic and biochemical approaches have identified novel genetic and physical interactions with membrane-associated ERAD machineries.
