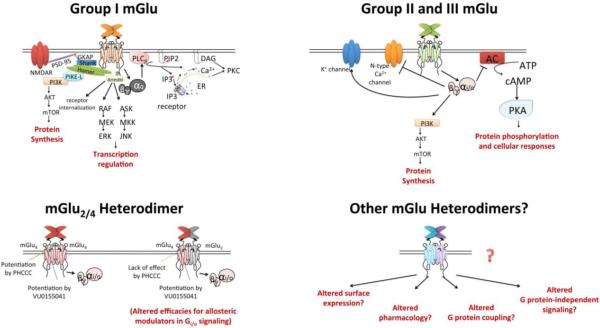
Figure 1.
The group I, II and III mGlu receptors induce signal transduction through both G protein-dependent and independent pathways. mGlu2/4 heterodimerization differentially regulates the efficacies of mGlu4 PAMs binding to separate allosteric pockets, whereas the expression, signaling and pharmacology of other mGlu heteromers remain unexplored. GKAP, guanylate kinase-associated protein; PSD-95, postsynaptic density protein 95; NMDAR, N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; PIKE-L, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase enhancer-long; AKT, protein kinase B; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; ASK, apoptosis signal-regulating kinase; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinases; PIP2, Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; DAG, diacyl-glycerol; IP3, inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; PKC, protein kinase C; AC, adenylate cyclase; PKA, protein kinase A.