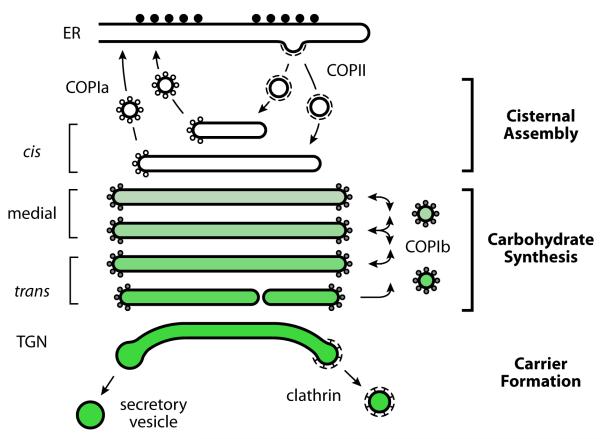
Figure 1.
We propose that the Golgi can be divided into three stages of maturation. During the Cisternal Assembly stage, COPII vesicles bud from the ER and fuse with one another to generate a new Golgi cisterna, while COPIa vesicles bud from this nascent cisterna to recycle trafficking proteins and resident ER proteins to the ER. This stage includes cis-Golgi cisternae, as well as ERGIC membranes in animal cells. During the Carbohydrate Synthesis stage, most of the oligosaccharide remodeling reactions take place, and resident Golgi proteins are transferred between cisternae by COPIb vesicles. This stage includes cisternae that are often designated medial and trans. During the Carrier Formation stage, the cisterna disintegrates to produce cargo carriers that include clathrin-coated and secretory vesicles. This stage includes cisternae that are traditionally designated TGN. Adapted from [24].