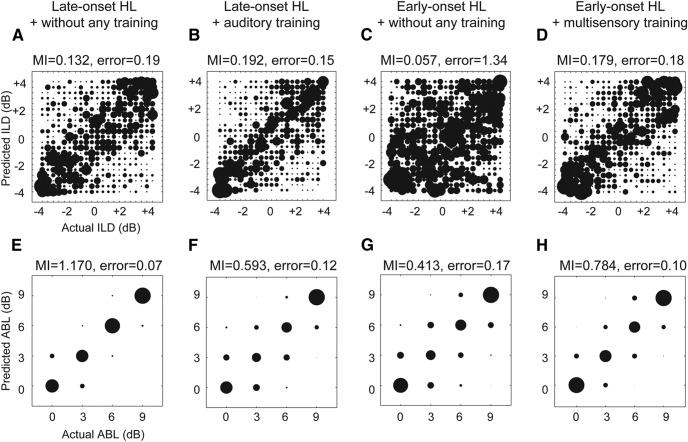
Figure 9.
Results of the MDA of ILD and ABL coding by auditory cortical neurons in ferrets with BiCIs, grouped by age at onset of hearing loss and training history. The size of each circle in the bubble plots is proportional to the number of classifications made for a given stimulus value. The x- and y-axes in each plot represent the true and classifier-assigned identities, respectively. A–D, ILD coding in acutely deafened and implanted adult animals that did not receive behavioral training (A), and in animals with late-onset hearing loss followed by cochlear implantation and auditory training (B). Early-onset hearing loss followed by cochlear implantation in adulthood without any training (C), and early-onset hearing loss followed by cochlear implantation in adulthood with auditory alone and then multisensory training (D). In the untrained animals with early-onset hearing loss (C), the ILD sensitivity of cortical units was poor, as indicated by the relatively large number and magnitude of classification errors, whereas training produced a significant increase in classification accuracy (D). The MI between model-predicted and actual ILD is shown above each confusion matrix. The mean absolute error associated with each classification is also indicated above each plot. E–H, ABL coding by auditory cortical neurons for the same four groups. MI for ABL coding is also indicated above each panel.