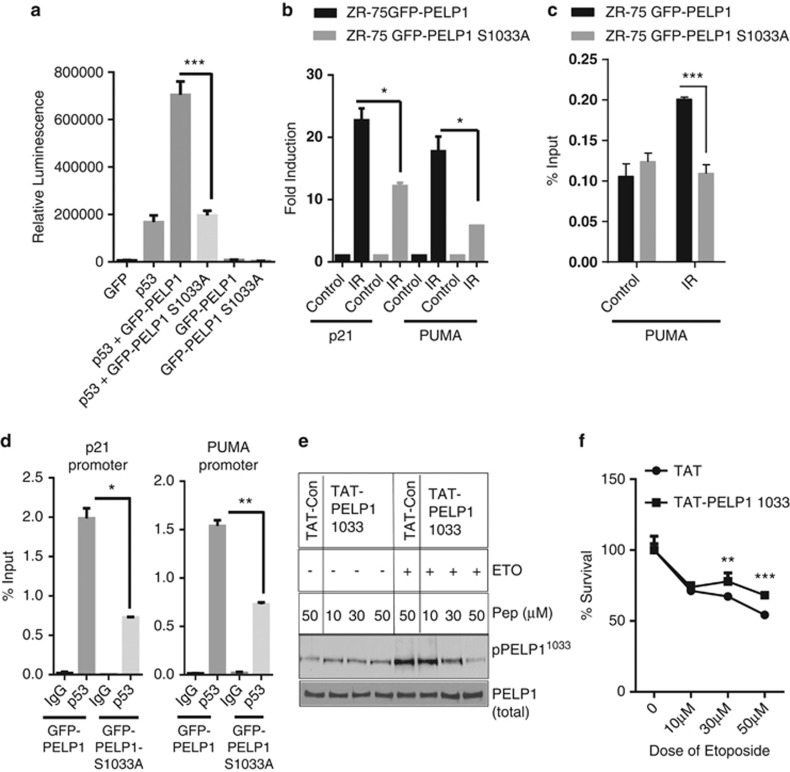
Figure 6.
Ser-1033 phosphorylation is needed for PELP1-mediated optimal p53 coactivation functions. (a) p53 null cells (H1299) were co-transfected with p53, p53-reporter and beta-galactosidase reporter plasmids with the GFP vector, GFP-PELP1 (WT) or GFP-PELP1S1033A (MT) plasmids. After 24 h of transfection, cells were treated with etoposide for 6 h and then luciferase activity was measured in the lysates and normalized with β-gal activity. Data shown are the means of ±S.E.M. performed in triplicate wells. ***P<0.001. (b) ZR75 cells expressing shRNA-resistant PELP1 WT or MT were transfected with PELP1-specific siRNA to downregulate endogenous PELP1. After 72 h, cells were treated with IR (10 Gy, 4 h), RNA was isolated and the status of p53 target genes was analyzed by RT-qPCR analysis. (c) ZR75 cells expressing GFP-PELP1-WT or GFP-PELP1-MT were treated with γ-radiation and ChIP analysis was performed using GFP epitope-specific antibodies and the status of PELP1 recruitment was analyzed by using RT-qPCR with PUMA promoter-specific primers. (d) ZR75 cells expressing GFP-PELP1-WT or GFP-PELP1-MT were treated with γ-radiation (10 Gy, 1 h) and ChIP analysis was performed using p53-specific antibodies and the status of p53 recruitment was analyzed by using RT-qPCR with p21 and PUMA promoter-specific primers. (e) ZR75 cells were pre-treated with indicated concentrations of TAT control or TAT-PELP1-1033 peptide. Cells were treated with or without etoposide and the PELP1 phosphorylation was analyzed via western blotting using the PELP1 Ser-1033 phospho antibody. (f) ZR75 cells were pre-treated with TAT control or TAT-PELP1-1033 peptide (50 μM) followed by treatment with different doses of etoposide for 48 h, and cytotoxicity was measured using MTT assays. Error bar depicts S.E. from triplicate experiments. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001