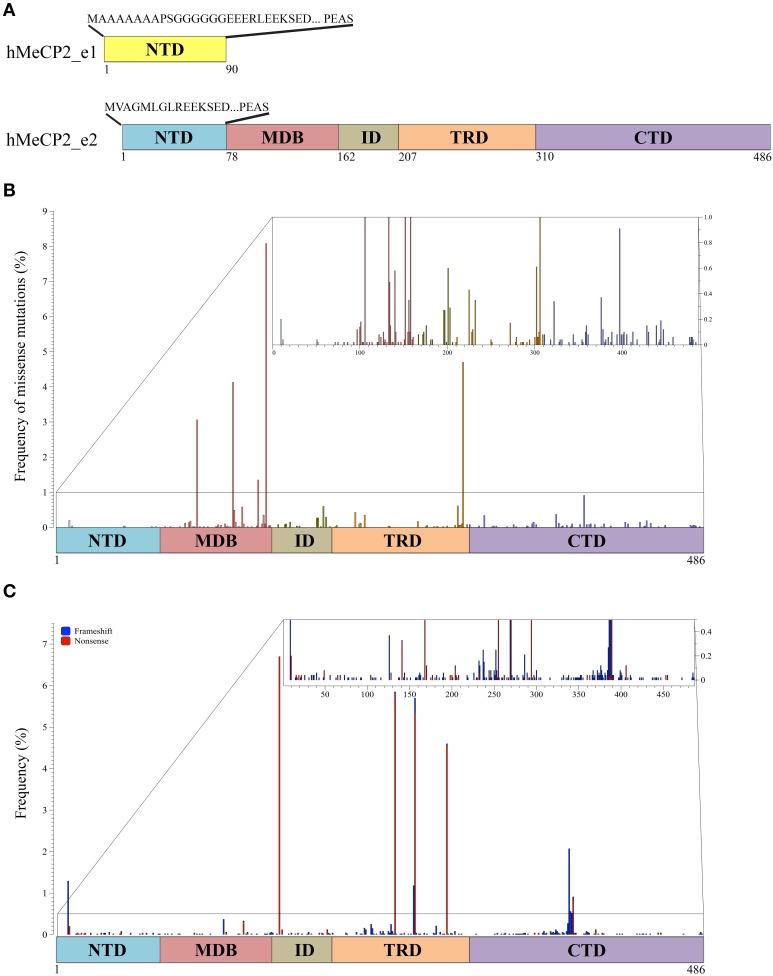
Figure 1.
MeCP2 isoforms and pathogenic mutations. (A) Two MeCP2 isoforms, MeCP2_e1 and MeCP2_e2, are generated by alternative splicing originating two distinct N-terminal regions. MeCP2_e1 is 498 amino acids long and contains a N-terminal domain (NTD, yellow) of 90 amino acids of which the first 21 are distinct, whereas MeCP2_e2, formed by 486 amino acids, has 9 unique amino acids in its NTD (blue). MeCP2 is constituted by five sub-domains: NTD, MBD (methyl-CpG binding domain), ID (intervening domain), TRD (transcriptional repression domain, CTD (C-terminal domain); below the MeCP2_e2 isoform is shown the amino acid numbers of the different domains. (B) Schematic illustration showing the localization and the frequency of pathogenic missense mutations within MeCP2. The small inset shows in details the mutation frequency between 0 and 1%. The colors of the vertical bars correspond to the color code of the distinct MeCP2 subdomains. (C) Localization and frequency of non-sense and truncating MECP2 mutations. Frameshift mutations are shown in blue and non-sense mutations in red. The small inset shows in details the mutation frequency between 0 and 1%.