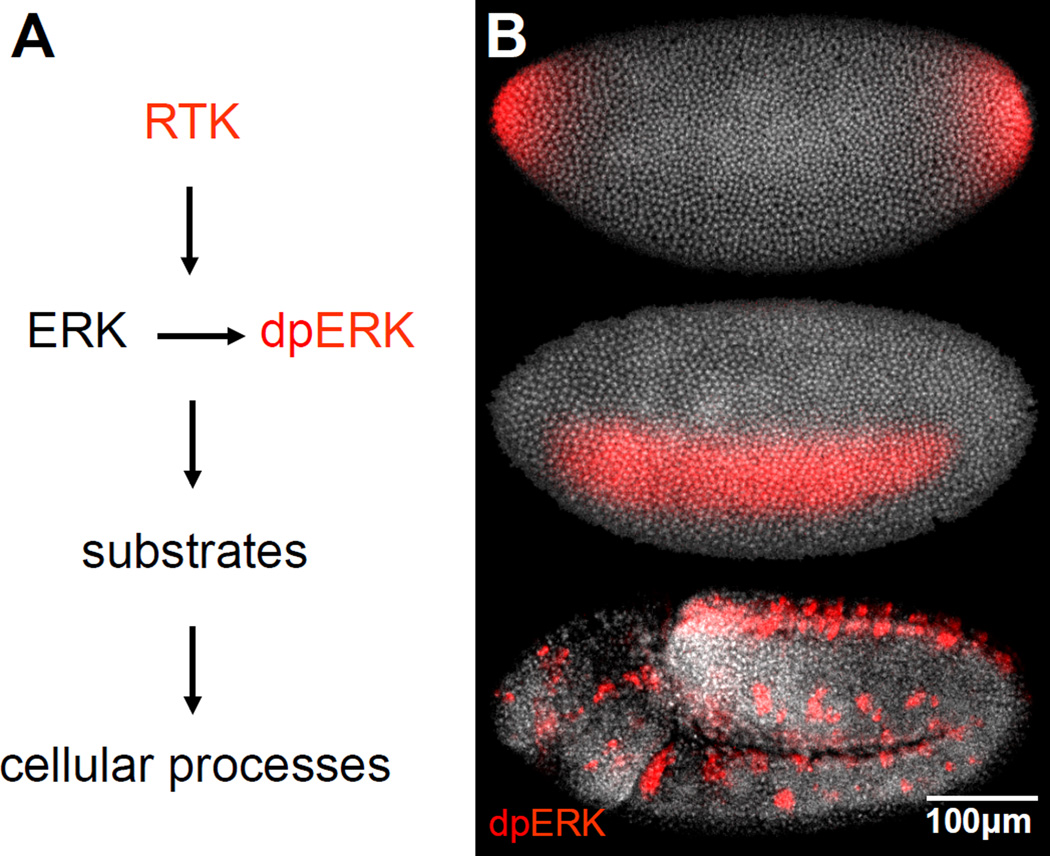
Figure 2.
Patterns of ERK activation in organisms. (A) ERK activation requires its phosphorylation by MEK. Active ERK controls cellular processes by phosphorylating multiple substrates. (B) Active ERK (red) at three different time points in Drosophila embryos. Active ERK is first detected at the embryonic poles, where it specifies the nonsegmented terminal regions of the future larva. Within the next 30 minutes, ERK is activated in a lateral domain corresponding to the presumptive neurogenic ectoderm. After gastrulation, ERK is active along the ventral midline and in tracheal pits.