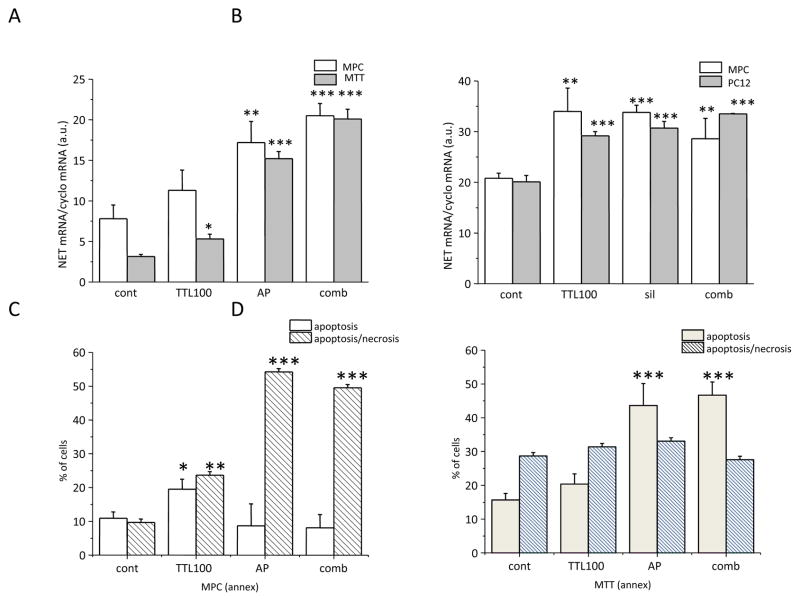
Figure 5.
Effect of NF-κB antisense peptide (AP; A) and NF-κB mRNA silencing (sil; B) on NET mRNA. In accordance with the TTL effect, AP and/or sil also significantly increased NET mRNA (A, B). In order to show that TTL acts through the NF-κB site, NET mRNA was measured in cells treated with a combination of both TTL and AP or sil (comb). In this combination, no additional increase in NET mRNA was observed as compared to TTL or AP or sil (A, B). Thus, based on this result we propose that TTL might act through the inhibition of the NF-κB site. In order to estimate the effect of AP on apoptosis and necrosis, we measured annexin V and propidium iodide in all tested samples (C, D). While AP significantly increased apoptosis in MTT cells (D), in MPC cells the same amount of AP resulted in an increase in necrosis (C). Results are displayed as mean ± S.E.M. and represent an average of at least five parallels from two independent cultivations. Statistical significance compared to control represents * - p>0.05, ** - p>0.01 and *** - p>0.001.