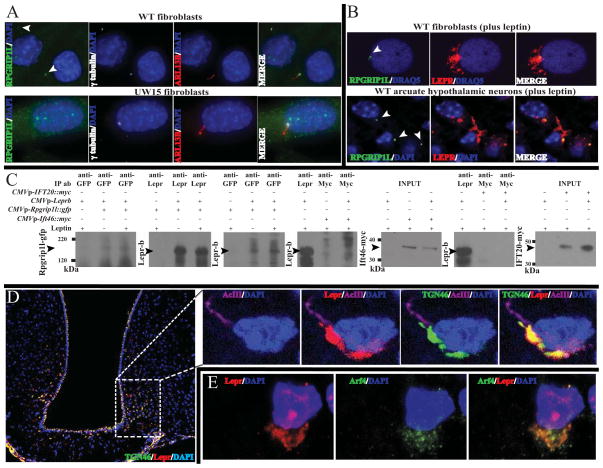
Fig. 6. Co-localization of RPGRIP1L, Lepr, Tgn46 and Arf4.
(A) Localization of endogenous RPGRIP1L in ciliated wild type primary fibroblasts. Increased gain of the green channel confirmed the absence of RPGRIP1L at the transition zone of fibroblasts from patient UW15 segregating for biallelic mutations in RPGRIP1L. Arrows point at the transition zone.(B) RPGRIP1L co-localizes with Lepr-b transiently expressed in primary fibroblasts from an unaffected subject, as well as endogenous Leprin arcuate neurons. See also Movie S3. (C) Increased levels of co-immunoprecipitated Lepr-b with GFP-tagged Rpgrip1l in the presence of leptin compared with proteins extracts from untreated primary fibroblasts from unaffected human subjects. Lepr-b did not co-immunoprecipitate with myc-tagged ciliary protein Ift46 or IFT20 in the presence or absence of leptin. (D) Subcellular co-localization by immunohistochemistry of Lepr and Tgn46 (See also Fig. S1M) or (E) Lepr and Arf4in the arcuate hypothalamus of mice stimulated with leptin.