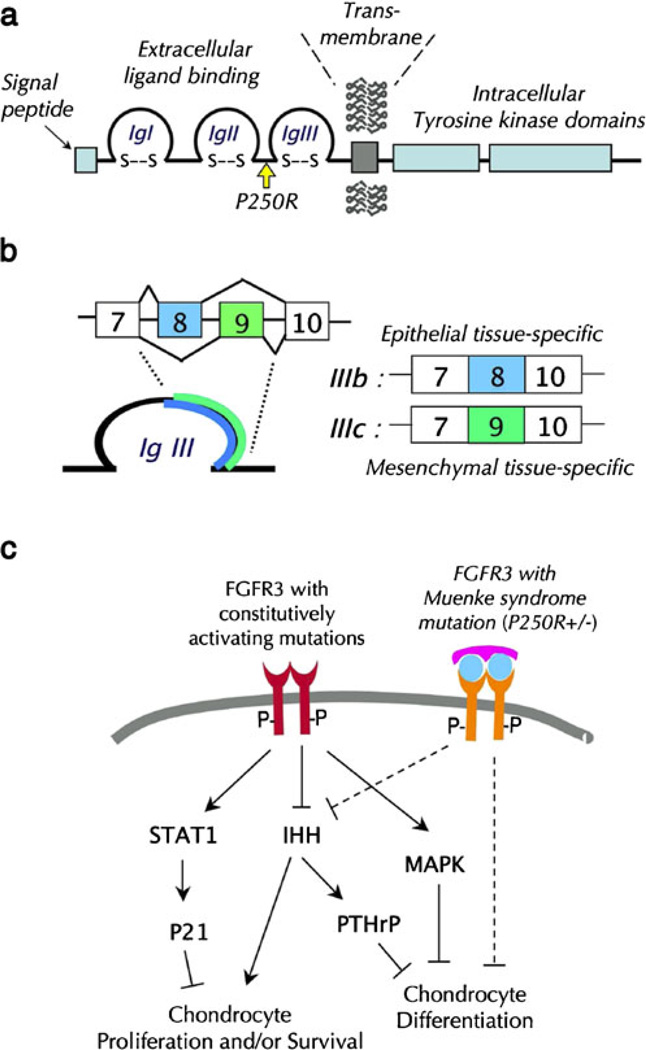
Fig. 2.
a A schematic diagram depicting the FGFR3 protein domains and the location of the Muenke syndrome mutation. b Alternatively splicing of exons 8 and 9 of the FGFR3 gene results in epithelia; tissuespecific IIIb isoform and mesenchymal tissue-specific IIIc isoforms. c Constitutively activating ligand-independent mutations of FGFR3 inhibit chondrogenic cell proliferation and/or survival and differentiation via activation of STAT1 [23], inhibition of IHH signaling [7], and sustained activation of MAPK [37, 55]. TheMuenke syndrome mutation, a ligand-dependent activating mutation, inhibits chondrocyte proliferation via IHH signaling and inhibits chondrocyte maturation [25, 54]