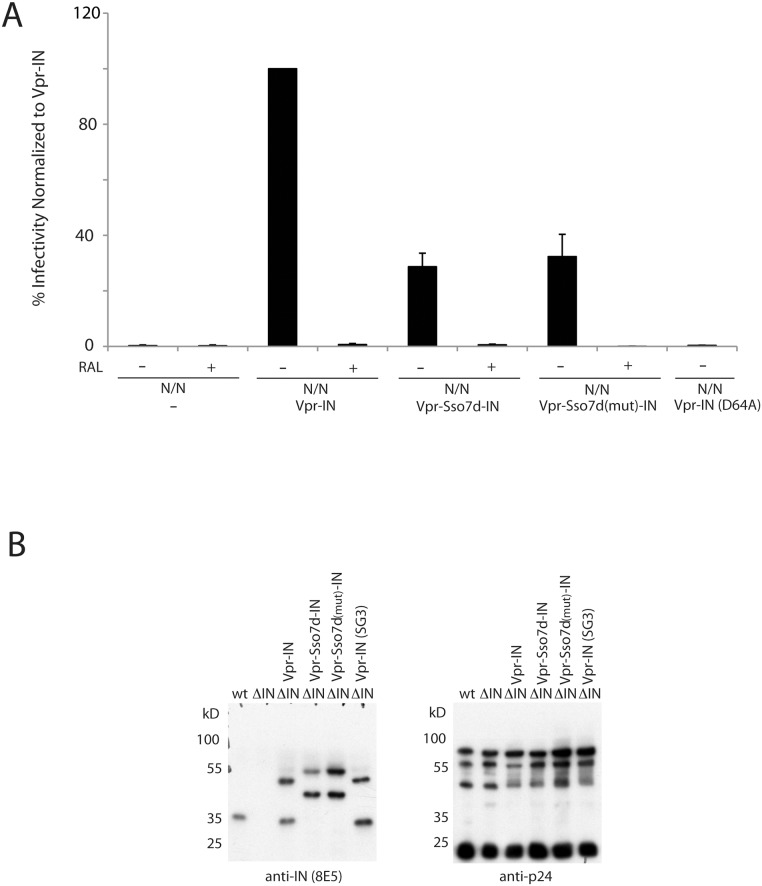
Figure 6. Sso7d-IN is functional in virions.
The assay is based on the ability of IN expressed as a Vpr fusion protein to transcomplement N/N virus lacking a functional integrase. A, HIV-1 infectivity normalized to the level obtained with Vpr-IN complementation. The Vpr fusions used for complementation and the infections that were conducted in the presence of RAL are indicated. Sso7d(mut) contains the mutations W24A and R43E which abrogate DNA binding. Graphed are averages with standard deviation for n = 3 (infections with RAL or Vpr-IN-D64A) or n = 6 independent experiments. B, Western blot of IN deletion mutant virus produced with indicated Vpr fusions probed for IN (left panel) and p24 (right panel). All Vpr-IN constructs yielded similar levels of packaged IN protein. The anti-IN antibody 8E5 recognizes the C-terminus (262–271) of IN [18] while the anti-p24 was from Abcam.