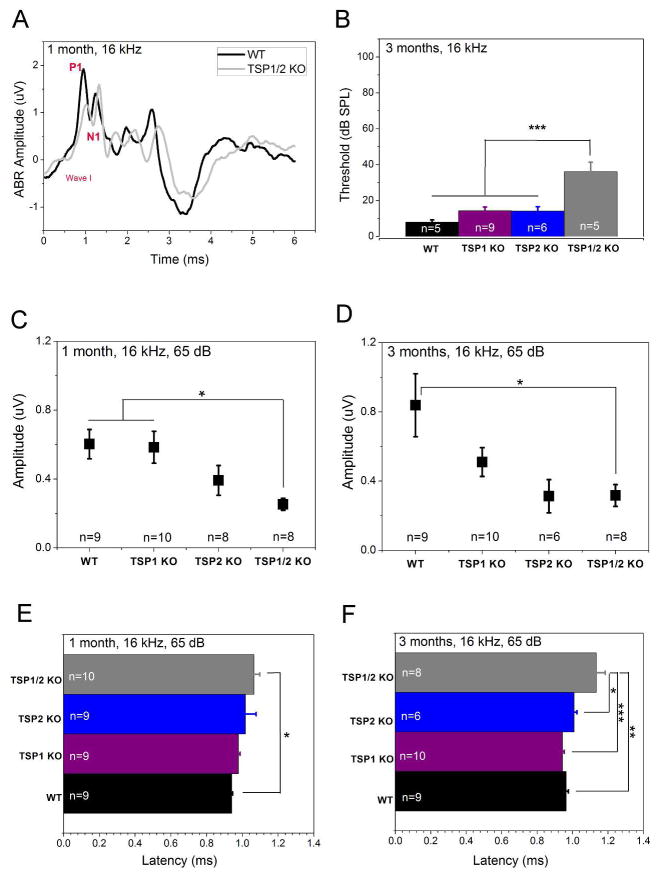
Figure 4.
Analysis of auditory nerve firing in TSP mutants at 1 month and 3 months of age. ABR wave I response amplitude and latency were analyzed at 65 dB for 16 kHz. Statistical analyses were performed using a one-way ANOVA followed by Scheffe’s post hoc test. A, Representative waveforms of WT (black line) and TSP1/2 mutants (grey line) at 1 month of age. Difference between P1 and N1 values indicate the amplitude of response. Distance time when stimulus was given (0 on the X axis) and time of response (P1 on the wave I) is the latency of the response. B, ABR thresholds in WT and TSP mutant mice at 16 kHz indicate no significant threshold shift in TSP1 or TSP2 mutants as compared to WT. C, ABR wave I amplitude was significantly reduced in TSP1/2 mutants as compared to WT at 1 month of age (P = 0.026). B and D, TSP1/2 KO had prolonged latency as compared to WT at 1 month (P = 0.031) (B) and 3 months (P = 0.001) (D) of age. C, at 3 months of age, amplitude of wave I in TSP1/2 mutants was significantly reduced (P = 0.038). Amplitude shift in TSP1 KOs was not significant. TSP2 mutants had an insignificant shift in amplitude at this age. N-value near indicated genotype gives the number of animals that were used for the experiment. Quantification data is presented as mean ± SEM. Significant differences are indicated by * for P < 0.05, ** for P < 0.01 or *** for P < 0.001.