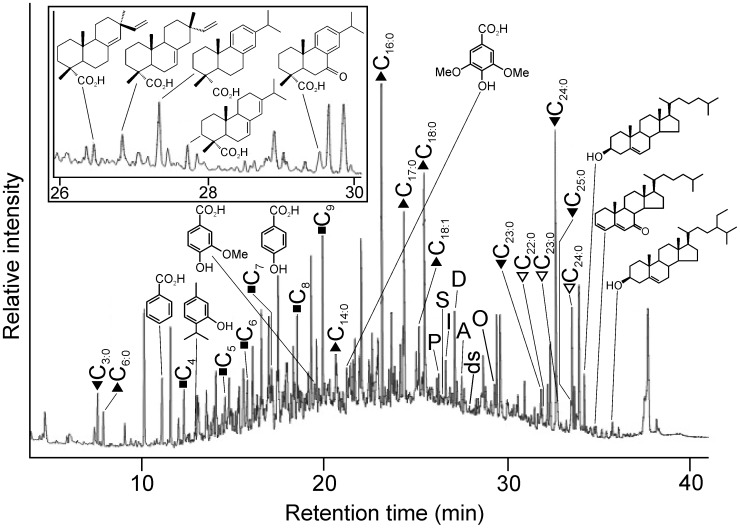
Figure 4. Reconstructed gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) total ion chromatogram (TIC) of the trimethylsilylated total lipid extract of 33.30.44 2.
Peak identities (‘n’ indicates carbon chain length; where shown, i indicates degree of unsaturation): filled triangles, Cn:i indicates fatty acids; filled squares, Cn indicates α,ù-dicarboxylic acids; filled inverted triangles, Cn:i indicates 2-hydroxy fatty acids; open inverted triangle, Cn:i indicates 2,3-dihydroxy fatty acid. Also shown are the structures of four aromatic acids identified: benzoic acid, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, vanillic acid (4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzoic acid) and syringic acid (4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoic acid); one monoterpenoid: thymol; six diterpenoids: pimaric acid (P), sandaracopimaric acid (S), isopimaric acid (I), dehydroabietic acid (D), abietic acid (A) and 7-oxo-dehydroabietic acid (O) (labeled as in Figure 3) and four steroidal compounds identified: stigmasta-3,5,22-triene, cholesterol, cholesta-3,5-dien-7-one and β-sitosterol; the letters ds represent a disaccharide. Inset displays a partial reconstructed GC-MS TIC of this sample focusing on the diterpenoid (resin) acids and showing the molecular structures of five of those identified: pimaric acid, isopimaric acid, dehydroabietic acid, abietic acid and 7-oxodehydroabietic acid.