Figure 2. Bacterial population density controlled by different RBS artificial quorum-sensing circuits.
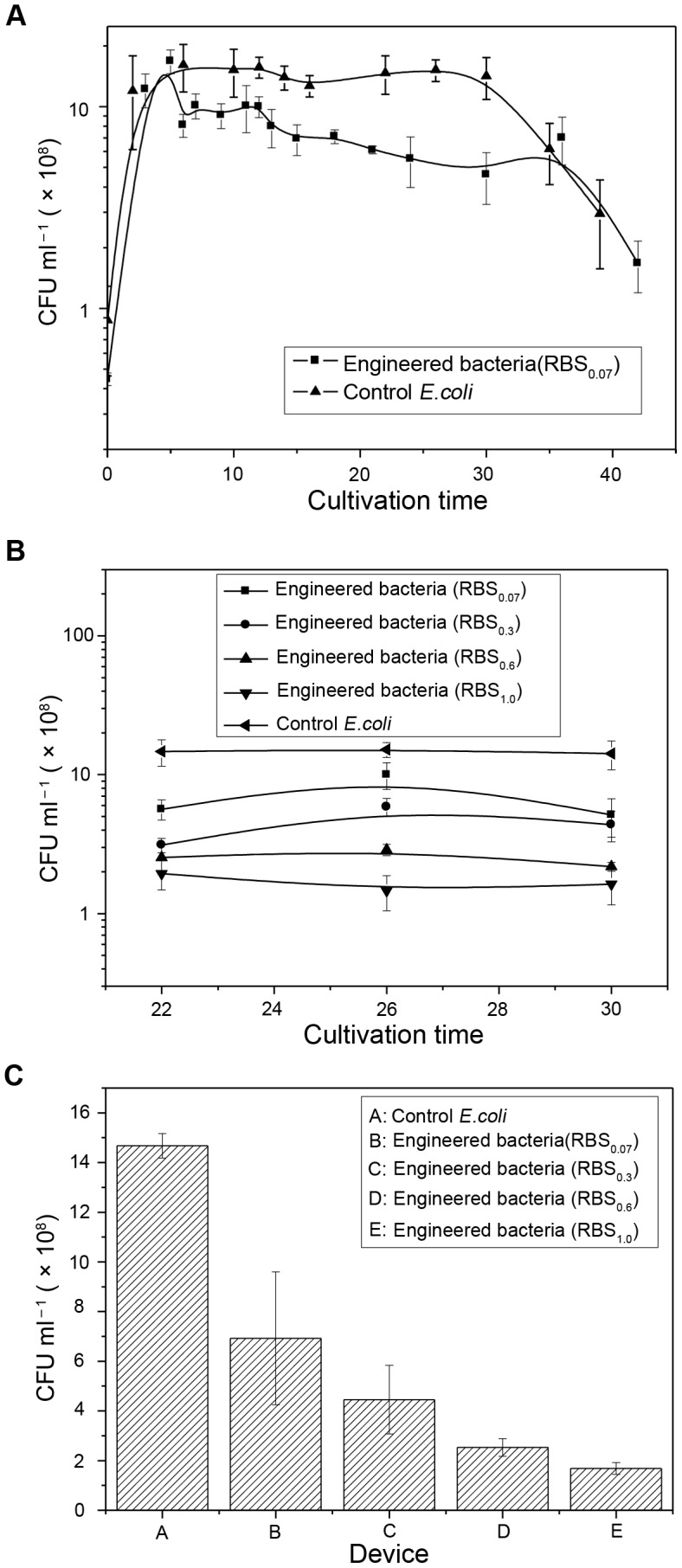
Note: The error bars represent the standard deviation of at least three replicates. (A) Curves for viable cell numbers of the engineered bacteria E. coli BL21(DE3) containing an RBS0.07 programmed bacterial death quorum-sensing circuit and control E. coli. The curve for engineered bacteria was different from that for control E. coli. And these differences were significant (t = 1.98 > t0.90, 17 = 1.74) during 6–30 h with 90% confidence interval using an independent samples t-test. At approximately 5 h, there was a dramatic decline in the number of viable engineered cells compared with control cells, after which the growth curve tended to level off after two small amplitude oscillations. The lower population density of the RBS0.07 engineered bacteria remained until its growth rate decreased after >30 h of culture. (B) Viable cell numbers at different times of steady state for four strains of engineered bacteria containing different RBS (RBS0.07, RBS0.3, RBS0.6, or RBS1.0) quorum-sensing circuits. (C) Final histogram for viable cell numbers of the four strains of engineered bacteria. This indicated that with an increase in RBS efficiency, viable cell numbers gradually decreased.
