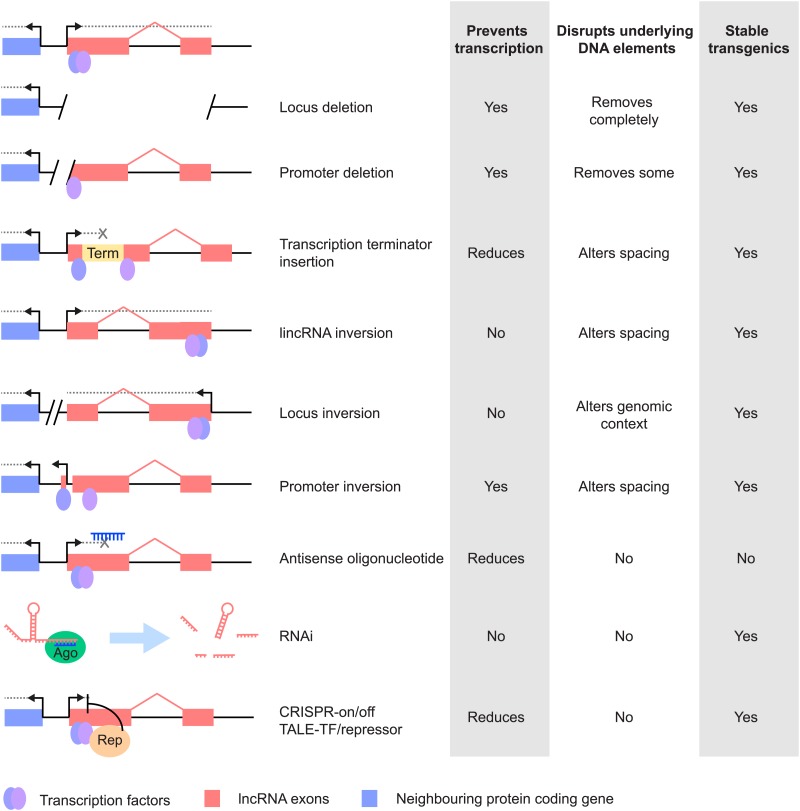
Figure 2. Different strategies for analysis of lncRNA loss-of-function. Strategies that have been used to alter lncRNA function are described pictorially, with the wild type situation on the top-most line.
The lncRNA locus is indicated in pink, neighbouring protein-coding gene in blue, transcription factor binding sites within it by blue and purple ovals, transcriptional terminator sequences in yellow (‘Term’) and the process of transcription by grey dotted lines. Antisense oligonucleotides are able to bind to nascent RNA transcripts and trigger RNase H mediated degradation of the transcript in the nucleus. RNAi is elicited by short RNA species that bind to argonaute proteins (Ago, green oval) within the cell. This complex recognises complementary lncRNA molecules in the cytoplasm, and triggers their destabilisation by the endogenous cellular machinery. The CRISPR and TALE systems use designer DNA binding factors to recruit repressor or activator domains (orange oval) to the lncRNA to affect transcriptional initiation. The effects of each strategy upon the process of transcription and presence of underlying DNA elements such as transcription factor binding sites are indicated. The possibility of generating stable transgenic animals to investigate phenotypes throughout development is also noted.