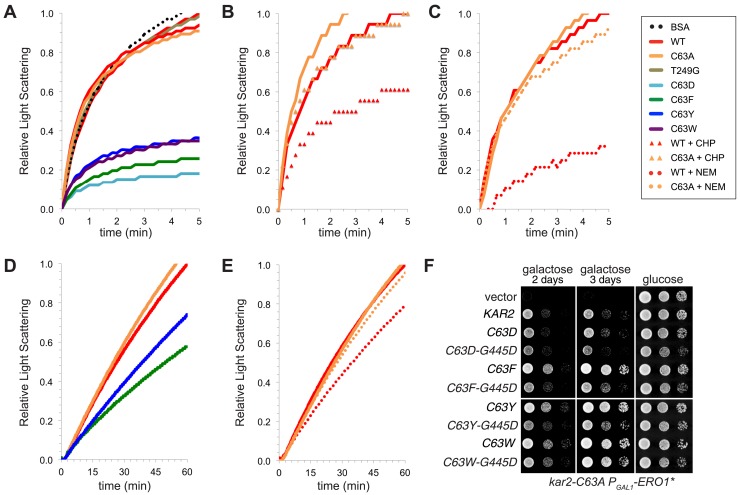
Figure 8. BiP cysteine mutants that protect cells during oxidative stress are more effective than wild-type BiP in suppressing polypeptide aggregation.
(A–C) Denatured rhodanese was diluted to a final concentration of 1 µM in the presence of 4 µM BSA or wild-type, mutant, peroxide-treated, or alkylated BiP. Samples in panels B and C were mock treated to match the CHP or NEM-treatment. Rhodanese aggregation was followed by monitoring light scattering at 320 nm over a period of 5 min (D and E) After denaturation in 6 M guanidine and 40 mM DTT, IgY was diluted to final concentration of 0.7 µM at 45°C in the presence or absence of 0.7 µM wild-type, mutant, or alkylated BiP. IgY aggregation was followed by monitoring light scattering at 360 nm over a period of 60 min. Data in panels A–E are representative traces from at least three trials. (F) CSY278 containing plasmids pCS681, pCS802, pJW5, pCS687, pCS844, pCS688, pCS845, pCS750, pCS846, or empty vector were spotted on SMM-leu or SMM Gal-leu plates, and plates were incubated at 37°C for 2 d (glucose) or 2-3 d (galactose).