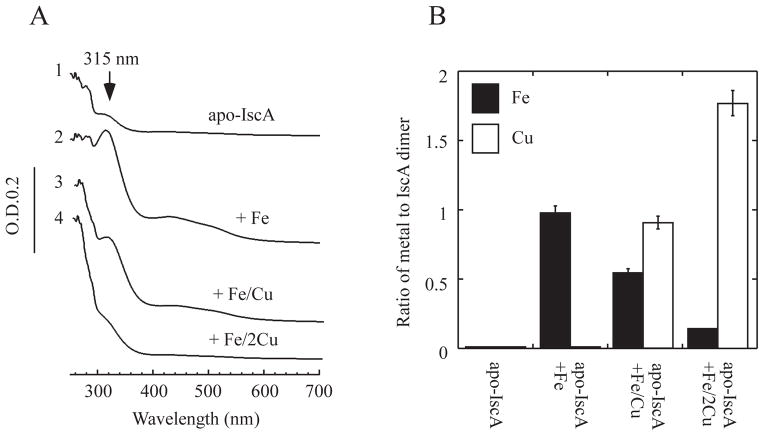
Figure 5. Excess copper competes with iron for the metal binding sites in IscA.
A), copper competes for the iron binding site in IscA. Apo-IscA (50 μM dimer) (spectrum 1) was incubated with Fe(NH4)2 (SO4)2 (100 μM) (spectrum 2), Fe(NH4)2 (SO4)2 (100 μM) and CuSO4 (100 μM) (spectrum 3), or Fe(NH4)2 (SO4)2 (100 μM) and CuSO4 (200 μM) (spectrum 4) in the presence of dithiothreitol (2 mM) at room temperature for 15 min. IscA was re-purified from the incubation solutions and subjected to UV-visible absorption measurements. B), iron and copper content analyses of re-purified IscA. The iron and copper content of re-purified IscA proteins from panel A) were analyzed and plotted as the ratio of metal to IscA dimer. The protein concentration was determined from the samples after incubation without metal ions. The results are presented as the mean ± standard deviations.