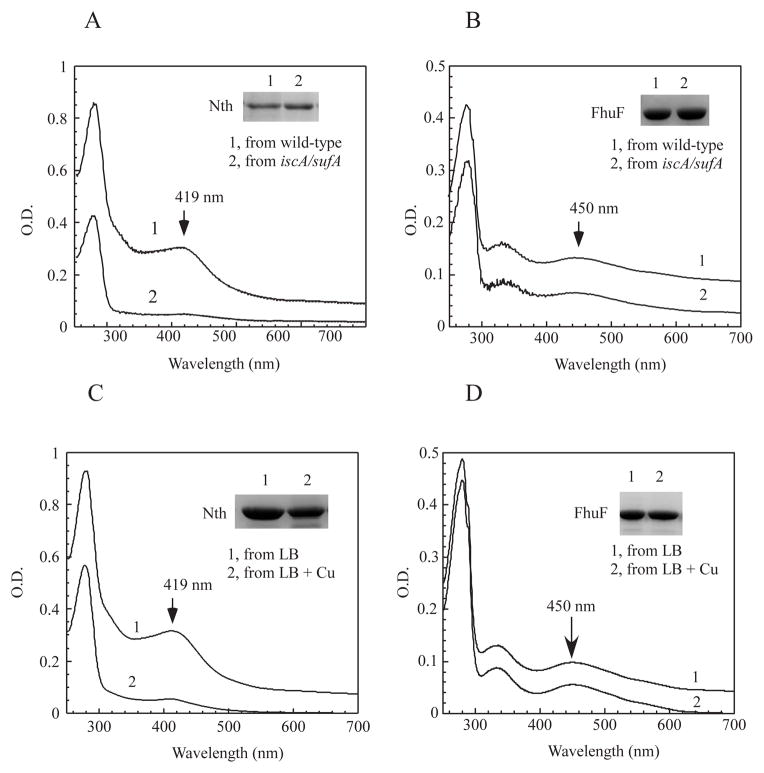
Figure 7. Copper selectively inhibits the [4Fe-4S] cluster assembly in the E. coli cells.
A), UV-visible absorption spectra of recombinant endonuclease III (Nth) (~ 30 μM) purified from the E. coli wild-type cells (spectrum 1) and the mutant cells with deletion of IscA/SufA (spectrum 2) grown in LB media under aerobic growth conditions. The absorption peak at 419 nm indicates the [4Fe-4S] cluster of endonuclease III. B), UV-visible absorption spectra of recombinant FhuF (~ 8 μM) purified from the E. coli wild-type cells (spectrum 1) and the mutant cells with deletion of IscA/SufA (spectrum 2) grown in LB media under aerobic growth conditions. The absorption peak at 450 nm indicates the [2Fe-2S] cluster of FhuF. C), UV-visible absorption spectra of recombinant endonuclease III (Nth) (~ 22 μM) purified from the E. coli copA/cueO/cusA mutant cells supplemented with 0 (spectrum 1) or 200 μM (spectrum 2) CuSO4 in LB media under aerobic growth conditions. D), UV-visible absorption spectra of recombinant ferric iron reductase FhuF (~ 5 μM) purified from the E. coli copA/cueO/cusA mutant cells supplemented with 0 (spectrum 1) or 200 μM (spectrum 2) CuSO4 in LB media under aerobic growth conditions. Insert in each panel is a photograph of SDS PAGE gel of purified proteins.