Fig. 4.
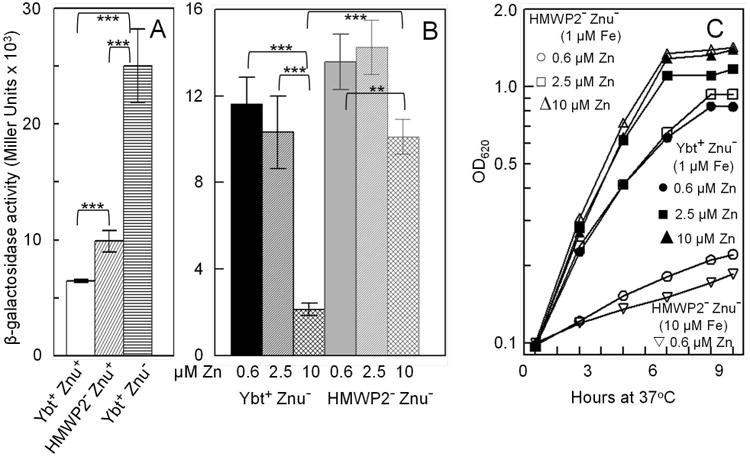
An irp2 mutation in Y. pestis results in lower intracellular Zn2+ levels (A and B) and increases the concentration of exogenous Zn2+ required to stimulate growth (C). The β-galactosidase activities shown (A and B) are averages (with standard deviations) of replicate samples from two independent cultures. Statistical significances were calculated using the Student's two tailed t-test; p = <0.001 - ***; p = < 0.005 - **. Growth curves (C) shown are from one experiment that is representative of two or more independent experiments. Strains were grown in cPMH2 at 37°C unsupplemented (A) or with increasing levels of ZnCl2 (B and C). cPMH was also supplemented with 1.0 μM FeCl3 (B) or indicated FeCl3 concentrations (C). Strains: KIM6+ (Ybt+ Znu+); KIM6-2046.1 (HMWP2- [irp2∷kan] Znu+); KIM6-2077+ (Ybt+ Znu- [ΔznuBC]); KIM6-2077.7 (HMWP2- [irp2∷kan] Znu- [ΔznuBC]). In A and B, all strains carry pEUZnu1 which encodes the znuA∷lacZ transcriptional reporter.
