Figure 4.
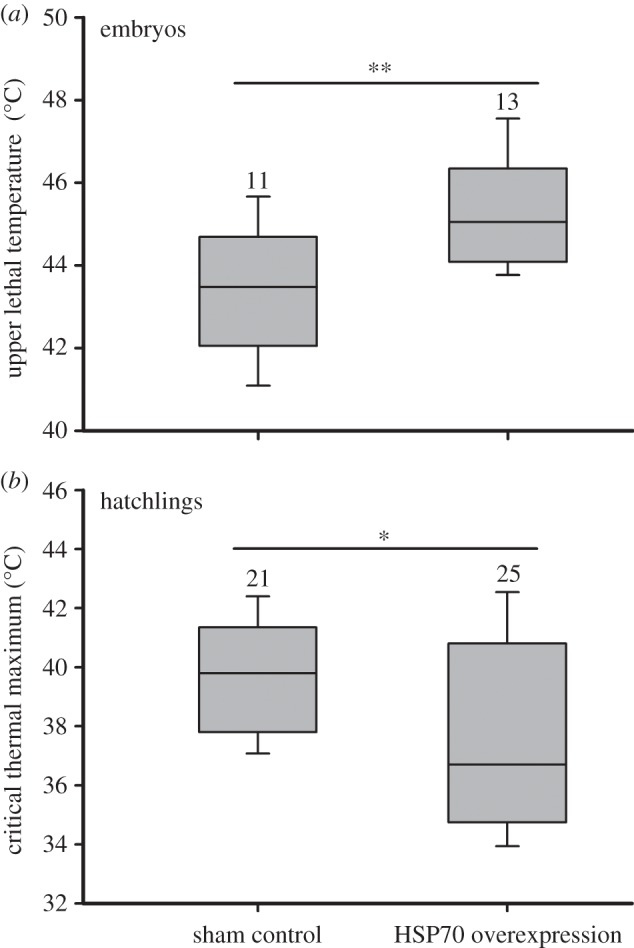
The upper lethal temperature of (a) embryos and (b) the critical thermal maximum of hatchlings from different HSP70 expression treatments in Pelodiscus sinensis. The eggs from HSP70 overexpression treatments were injected with pIRESPsHsp70, whereas those from the shame control with pIRES2-EGFP. For embryos, heart rate was monitored, and the highest temperature with a detectable heart rate was used as the critical thermal maximum. For hatchlings, body temperature associated with a transient loss of righting response at high temperature was used for the critical thermal maximum. Statistical significance between groups was calculated by Student's t test (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01). Data are shown as means ± s.e. Numbers above the error bars are sample size.
