Fig. 4.
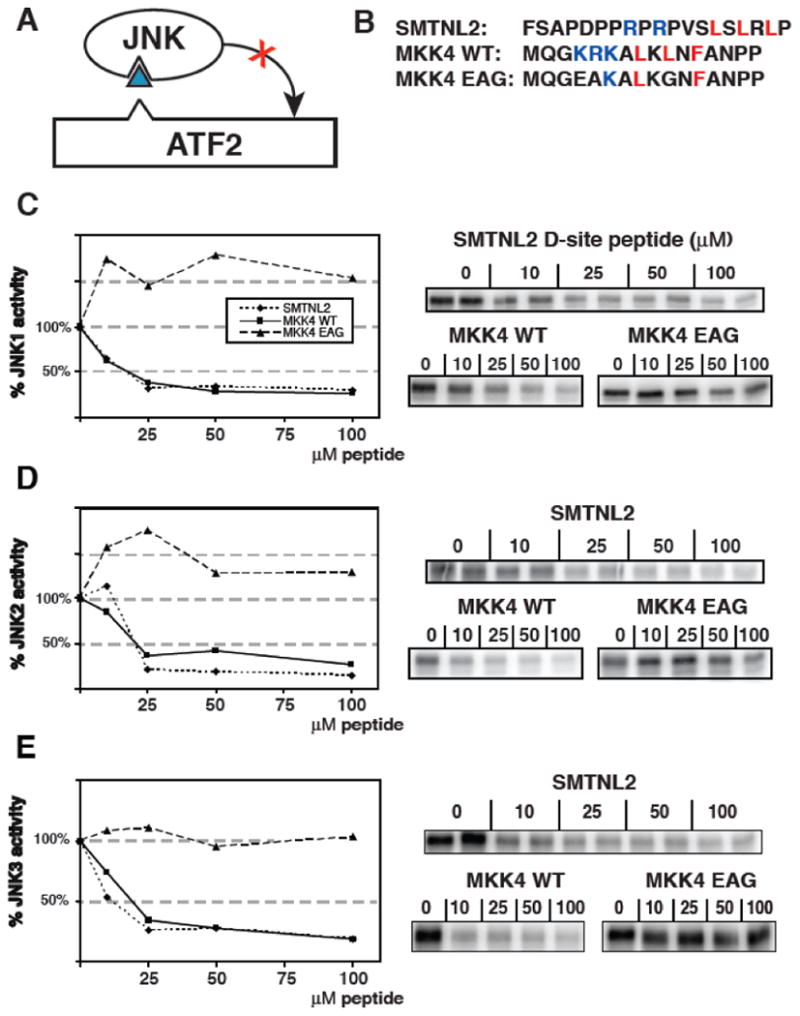
Inhibition of JNK phosphorylation of ATF2 by an SMTNL2 D-site peptide. A) D-site peptides (triangle) were used to inhibit JNK-mediated phosphorylation of the ATF transcription factor. B) Sequence of the D-site peptides used. C-E) Purified GST-ATF2 (0.5 μM) was incubated with 2.5 nM purified active JNK1 and [γ-32P] ATP for 30 min in the absence or presence of the specified concentrations of the indicated peptides. Phosphate incorporation into ATF2 was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and quantified on a phosphorimager. Results are plotted as a percent phosphorylation relative to that observed in the absence of any added peptide. Data are the average of three experiments, with duplicate points in each experiment. An autoradiogram of a representative experiment is shown on the right. D) As in C, except that the enzyme was purified active JNK2 (2.5 nM) (E) As in C, except that the enzyme was purified active JNK3 (2.5 nM).
