Figure 4.
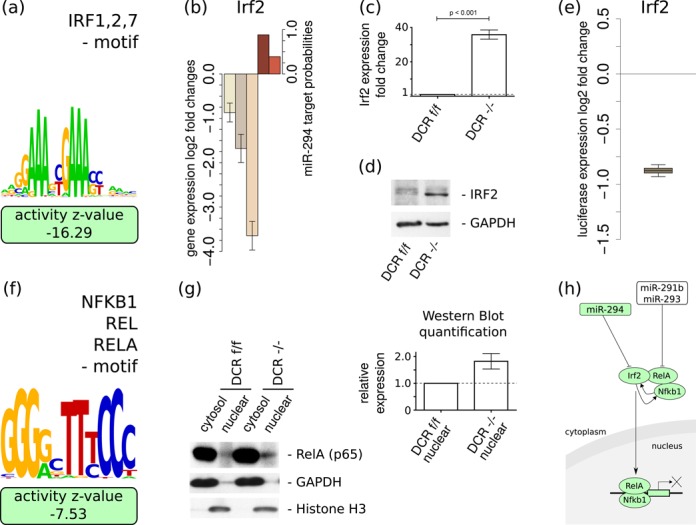
miR-294 targets the Irf2 TF and modulates ‘IRF1,2,7’ and ‘NFKB1_REL_RELA’ activities—(a) The activity of the ‘IRF1,2,7’ motif is strongly decreased in the presence of miR-294. (b) The expression of Irf2 is downregulated within all analysed data sets (±1.96*SEM; n = 3) and Irf2 is predicted by ElMMo and TargetScan to be a direct target of miR-294 (color scheme as in Figure 3). Low levels of Irf2 mRNA (c) and protein (d) in DCRflox/flox ES cells compared to miRNA deficient DCR−/ − ESCs are observed with qRT-PCR and western blot, respectively. qRT-PCR experiments were run in triplicate (± SEM; n = 3). (e) The luciferase reporter construct carrying the Irf2 3′UTR shows a strong response to miR-294 co-transfection compared to a similar construct but with a mutated Irf2 target site (n = 9). (f) Sequence logo of the ‘NFKB1_REL_RELA’ motif that is associated with the canonical NF-κB pathway and that exhibits a significant decrease in activity in the presence of miR-294. (g) Western blots of RelA, GAPDH and Histone H3 in nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions in ESCs that do and do not express miRNAs. The densitometric quantification indicates an increased level of nuclear RelA in the DCR−/ − ESCs compared to DCRflox/flox ESCs (± SEM; n = 3). (h) Proposed model of the inhibitory effect of miR-290-295 cluster miRNAs on the canonical NF-κB pathway in pluripotent stem cells. Regulatory motifs are denoted by colored rectangles and individual genes by ovals. See text for the evidence of individual interactions.
