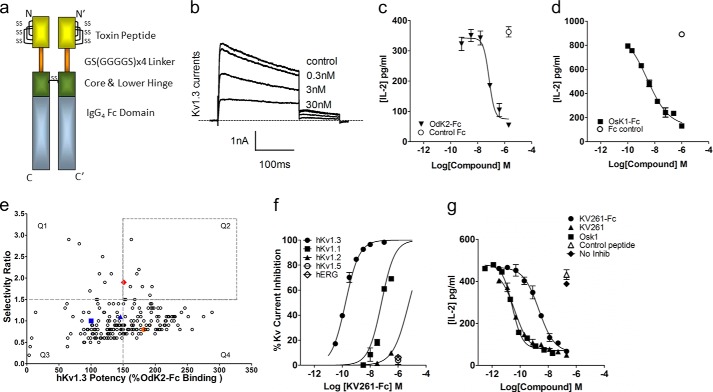
FIGURE 1.
Toxin peptide Fc fusion proteins are active, can be engineered for potency and selectivity, and inhibit in vitro human T cell activation. a, schematic representation of a toxin peptide-Fc fusion protein showing the Fc from a human IgG4 fused with the peptide C terminus with an intervening (G4S)4 linker. The peptide-Fc molecule is a covalent dimer with disulfide bonds (SS) between the adjoining core/lower hinge regions. The upper hinge region was removed from the Fc region for design of these fusions. The N and C designate the termini for Fc1 and N′ and C′ for Fc2 of the dimer, with predicted disulfide bonds designated (SS). b, OdK2-Fc fusion protein inhibits human Kv1.3 whole cell currents in a concentration-dependent manner in transfected CHO cells. c and d, inhibition of IL-2 production from anti-CD3/anti-CD28-stimulated human CD4+ T cells by OdK2-Fc and Osk1-Fc. e, primary screening results of chimera library variants (○) showing the relationship between Kv1.3 potency (% OdK2-Fc binding) and selectivity (binding ratio of Kv1.3/Kv1.1). OdK2-Fc parent control (■), OdK2-Fc parent recurrent in the library (▴), OsK1-Fc parent control (●), and lead variant KV1261-Fc (♦) are highlighted. Hits demonstrating improved selectivity as well as high Kv1.3 potency relative to OdK2-Fc are located in quadrant 2 (Q2). f, inhibition of Kv channels and hERG by KV261-Fc. These results indicate that the fusion protein is highly selective for Kv1.3. g, inhibition of IL-2 production from anti-CD3/anti-CD28-stimulated human CD4+ T cells by Osk1, KV261, and KV261-Fc.