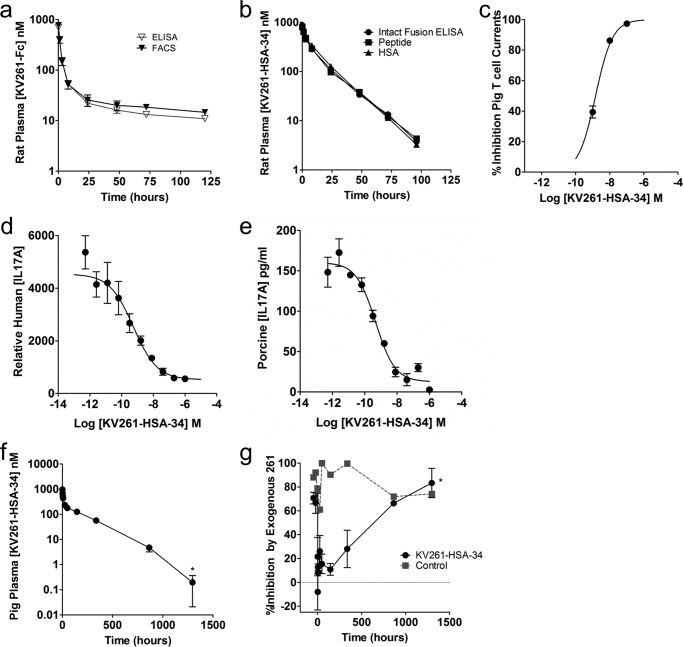
FIGURE 3.
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of KV261-fusions in rats and mini-pigs. a, KV261-Fc plasma levels in Sprague-Dawley rats were measured by detecting the Fc fragment (▿) and the intact fusion protein (▾). Rats (n = 3) were intravenously administered with KV261-Fc at 3.0 mg/kg, and KV261-Fc in vivo half-life was determined to be ∼72 h. b, KV261-HSA-34 plasma levels in Sprague-Dawley rats were measured by detecting intact fusion protein (●), the peptide (■), and the HSA fusion partner (▴). Rats were intravenously administered with 2.3 mg/kg of KV261-HSA-34. c, inhibition of Kv1.3 currents in minipig CD4+ T cells by KV261-HSA-34 measured using manual whole cell patch clamp electrophysiology. d, inhibition of IL-17A production from thapsigargin-stimulated human whole blood in vitro by KV261-HSA-34. e, inhibition of IL-17A production from thapsigargin-stimulated minipig whole blood in vitro by KV261-HSA-34. f, KV261-HSA-34 plasma levels in Yucatan minipigs after intravenous administration of KV261-HSA-34 at 2.3 mg/kg. Results shown are the average ± S.E. from four animals measured through day 36 and 2 animals at day 54. Half-life was calculated to be 5–7 days. g, pharmacodynamics of KV261-HSA-34 in minipigs was assessed in the same animals used in the pharmacokinetic study described in f. Blood samples collected from KV261-HSA-34 intravenously dosed animals (●) and a non-dosed control animal (■) were stimulated with thapsigargin ex vivo, and levels of induced IL-17A in whole blood were measured. The levels of thapsigargin-induced IL-17A correlate with Kv1.3 activity in blood. Thapsigargin-induced IL-17A was minimal in blood collected from KV261-HSA-34-injected minipigs from 1 min to 14 days post-administration. A gradual recovery of IL-17A was observed on days 36–54, correlating with the clearance of KV261-HSA-34 from circulation.