FIGURE 3.
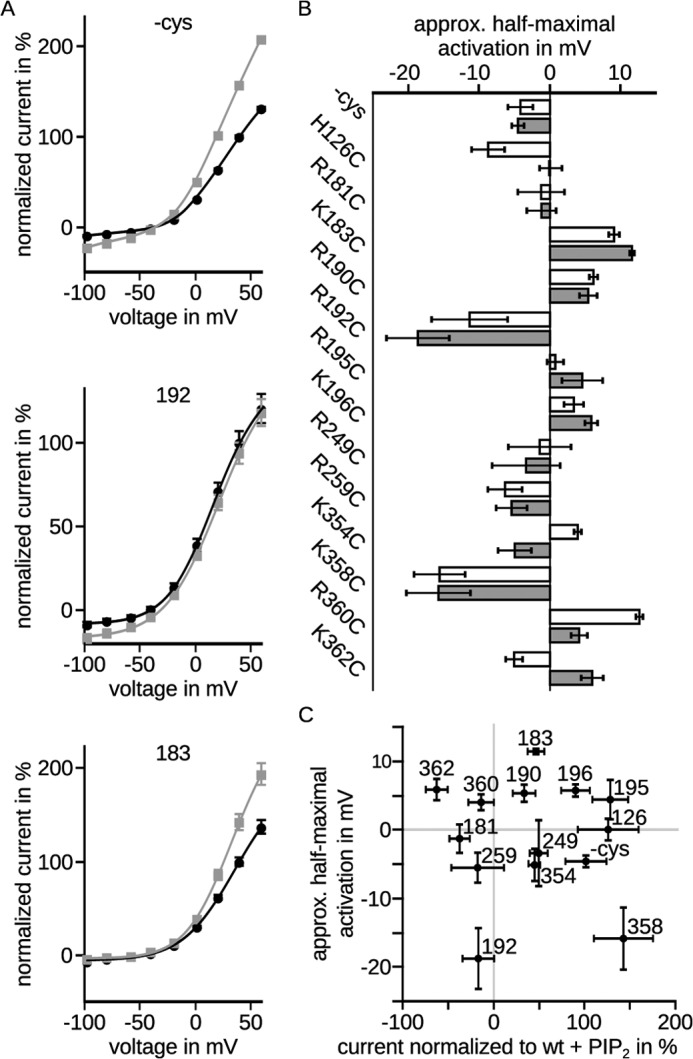
Conductivity-voltage relationships were differently affected by diC8-PIP2. Currents were recorded 3 days after injection. diC8-PIP2 was injected at least 30 min prior to the recordings. A, channel conductivity was calculated from current-voltage relationships obtained by the voltage protocol shown in Fig. 1B. The mean data ± S.E. were fit according to the Boltzmann equation multiplied with the driving force. Black, without diC8-PIP2; gray, with diC8-PIP2. Representative fits showed that saturation was not reached. B, half-maximal activation voltages ± fit error were unchanged (WT, R181C, R190C, R249C, R259C, and K358C) or shifted to positive (H126C, K183C, R195C, K196C, and K362C) or negative potentials (R192C, K354C, and R360C) by diC8-PIP2. White, without diC8-PIP2; gray, with diC8-PIP2. Significance could not be determined. C, half-maximal activation voltage ± fit error is compared with normalized current amplitudes ± S.E. shown in Fig. 2C. Clearly, no correlation between half-maximal activation voltage and normalized current amplitudes could be detected.
