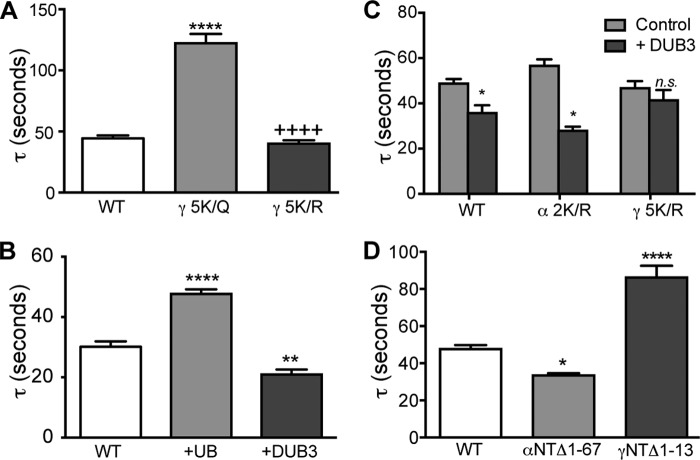
FIGURE 5.
γNT K-cluster is critical for regulation of ENaC proteolysis under ubiquitinating conditions. A, mutagenesis that eliminates any possibility of ubiquitination of the K-cluster and eliminates its basic charge (γNT-5K/Q) slows activation by chymotrypsin (increased Tau). However, mutation (γNT-5K/R) that preserves basic charge at the K-cluster has no effect on chymotrypsin stimulation. B, enhanced ubiquitinating conditions increased Tau (coexpressed ubiquitin (+UB, n = 14, p < 0.001)), whereas diminished ubiquitination conditions decreased Tau (coexpressed deubiquitinating enzyme 3 (+DUB3, n = 8, p < 0.01)) compared with WT ENaC alone (n = 14) stimulated by trypsin. C, deubiquitinating conditions increase the rate of WT ENaC stimulation (Tau decreased to 0.72 ± 0.04 of WT ENaC control without DUB3, n = 22, p < 0.001) but not in ENaC containing γNT 5 K/R (0.90 ± 0.09 of control without DUB3, n = 14, p = 0.20). In contrast, mutagenesis of potential ubiquitin targeted lysines in α-ENaC did not prevent stimulation of ENaC by DUB3 coexpression (Tau was 0.49 ± 0.03 of control without DUB3, n = 9, p < 0.001). D, deletion of residues 1–67 in α-ENaC caused a slight decrease in Tau (n = 21, p < 0.05), whereas deletion of residues 1–13 in the γNT to eliminate the K-cluster increased Tau (n = 25, p < 0.001).