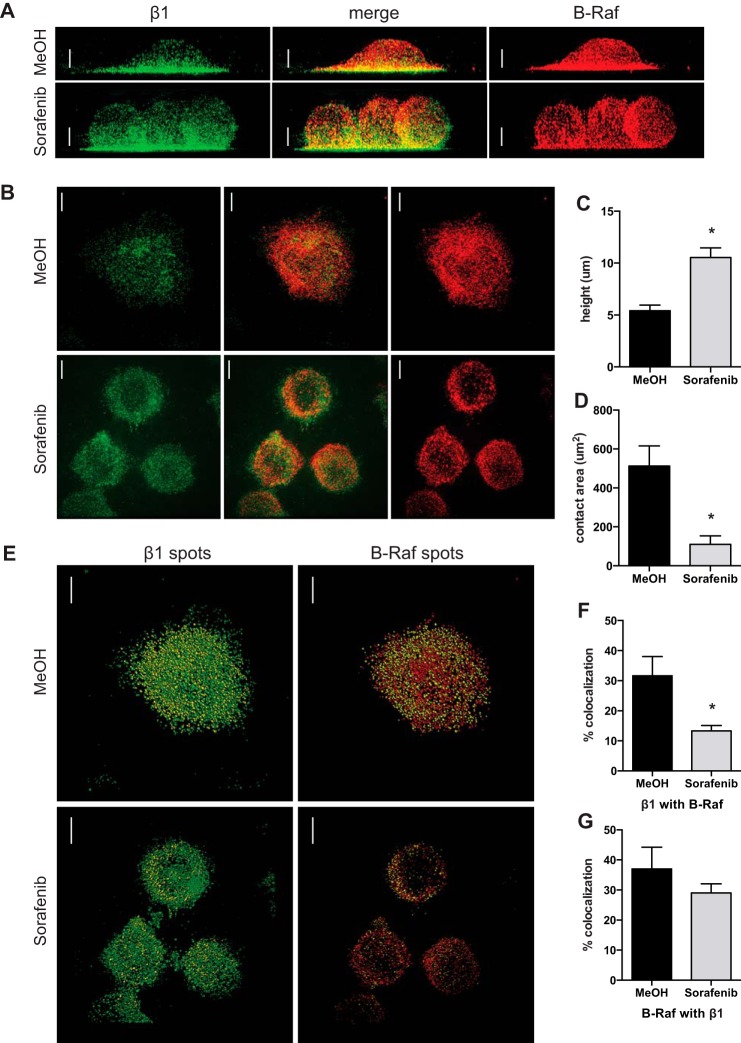
FIGURE 8.
Sorafenib inhibits cell spreading and β1 integrin colocalization with B-Raf after adhesion to VCAM-1. A and B, super-resolution immunofluorescence of β1 integrin (green) and B-Raf (red) of Jurkat cells incubated for 1 h with methanol vehicle control or sorafenib (50 nm) and then fixed after 10 min of adhesion to glass coverslips coated with VCAM-1 (10 μg/ml). A, representative maximum intensity projection of three-dimensional reconstructed images rotated by 90° to illustrate the height of cells; B, representative maximum intensity projection of the five z-sections closest to the interface with the coverslip to illustrate the area of contact with VCAM-1. C, images were analyzed for the height of the cells when rotated by 90° in three dimensions; D, the area of contact at the interface of the glass coverslip. E, colocalization of β1 integrin and B-Raf using the spot detection function of absolute fluorescence for total β1 integrin (green) and β1 integrin colocalized with B-Raf (yellow) (left) and total B-Raf (red) and B-Raf colocalized with β1 integrin (yellow) (right). The percentage of colocalization was determined by dividing the number of colocalized spots by the total number of spots for β1 integrin (F) and B-Raf (G). Data are shown from one experiment containing individual cells pretreated with methanol (n = 10) or sorafenib (n = 14), and the experiment was repeated with methanol (n = 10) and sorafenib (n = 12). Scale bars, 4 μm; error bars, S.E. *, p < 0.01 using Student's t test.