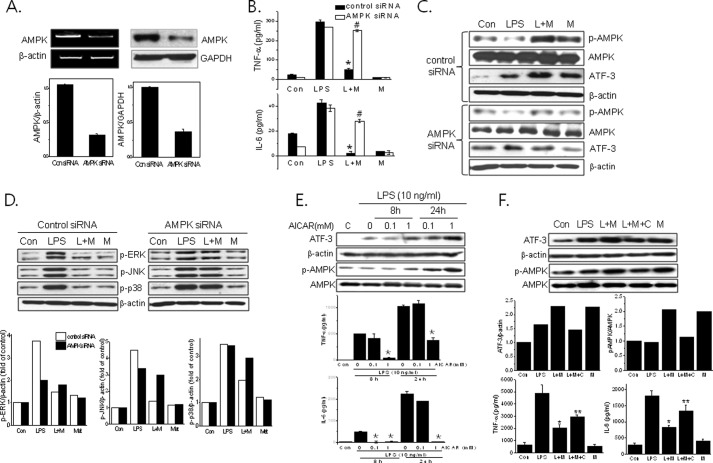
FIGURE 4.
Effects of AMPK knockdown on metformin action against LPS-induced inflammation. AMPK siRNA (100 nm) or control siRNA was transfected into primary macrophages, and the extent of AMPK knockdown was determined by RT-PCR (left panel) and Western blotting (right panel) (A). Then the cells were treated with metformin (M) (2 mm) for 20 h and then stimulated with LPS (L) for 4 h. Levels of TNF-α and IL-6 in culture media were determined by ELISA (B). The effects of AMPK siRNA on ATF-3 expression (C) and MAPK phosphorylation (D) were determined by Western blotting. The effects of AICAR (E) and compound C (F) on the levels of ATF-3, phospho-AMPK-α (Thr172) (p-AMPK) (Western blotting) and cytokines (ELISA) were determined. The experiment was repeated three times in triplicate. Results are expressed as means ± S.E. (error bars). *, p < 0.05 versus LPS alone; **, p < 0.05 versus LPS and metformin (L+M); #, p < 0.05 versus control siRNA. Con, control; p-ERK, phospho-ERK; p-p38, phospho-p38; p-JNK, phospho-JNK; Met, metformin.