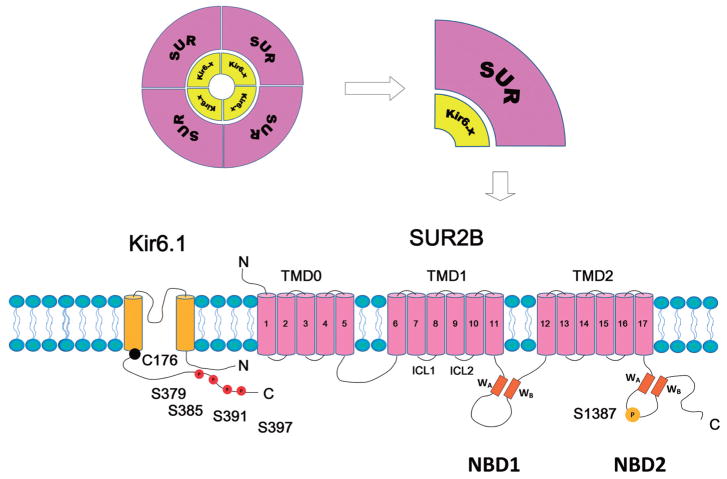
Fig. 1.
Molecular structure of the vascular KATP channel. KATP channels are octameric complexes formed by 4 Kir6 subunits (Kir6.x) and 4 accessory sulfonylurea receptor (SUR) subunits. The Kir6.x subunit has 2 transmembrane helixes. SUR subunit has 3 transmembrane domains (TMD0, 1 and 2). There are two intracellular loops linking the adjacent TMDs. Each intracellular loop contains a nucleotide binding domain (NBD1 and NBD2, respectively). A Walker A motif (WA), a Walker B motif (WB), and a linker region are located within the NBDs. The Ser379, Ser385, Ser391, and Ser397 at the distal C-terminus of Kir6.1 are PKC phosphorylation residues. The Ser1387 is PKA phosphorylation residue. The Cys176 in the transmembrane domain of Kir6.1 is the major residue accounting for the channel’s oxidant sensitivity.