Figure 3.
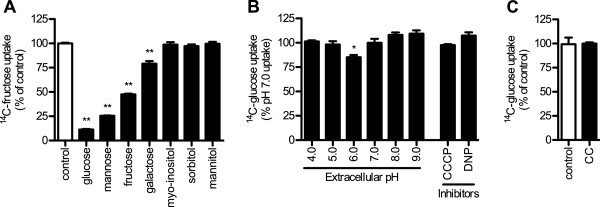
Functional characterization of ApST4 in whole yeast cells. Transport specificity of ApST4 was investigated by functional expression in EBY.VW4000 yeast cells (EBY-ST4 cells). (A) Inhibition of 14C-fructose uptake (50 mM initial extracellular concentration) in competition assays containing 100 mM unlabeled sugars (as indicated), uptake is displayed as percentage of no competing sugar (control). (B) pH dependence of 14C-glucose uptake in EBY-ST4 cells using indicated extracellular pH; and in the presence of transport inhibitors: 1 μM CCCP (Carbonyl cyanide 3-chlorophenylhydrazone) and 1 μM DNP (2,4-Dinitrophenol). All uptake is displayed as percentage pH 7.0 transport. (C) Na+ dependence of 14C-glucose uptake in EBY-ST4 cells using standard uptake buffer with addition of 50 mM NaCl (control), or in similar buffer were NaCl is replaced with an equimolar amount of choline chloride (CC). All uptake experiments were performed at 30°C and cells were collected by rapid-filtration after 10 min. Sugar uptake was determined by liquid scintillation counting. Transport was corrected for background uptake into control (−) cells transformed with an empty expression vector. Each value is the mean ± SEM, n = 3. Bars marked with asterisks are significantly different from controls. *P < 0.01 and **P < 0.001; one way-ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s post-test.
