Figure 5.
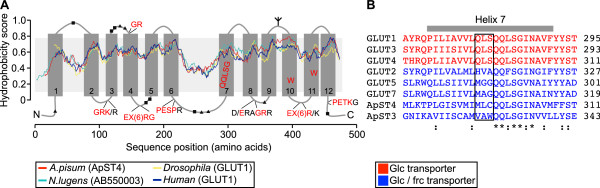
Sequence analysis of ApST4 and related GLUT transporters. (A) Alignment of hydrophobicity profiles for ApST4 (ACYPI001980) and GLUT class I transporters from: Nilaparvata lugens (AB550003); Drosophila melanogaster (CG1086); and Homo sapiens (GLUT1). Sequence position (in amino acids) and Kyte and Doolittle hydrophobicity score (normalized between 0–1) is shown on the x-axes and y-axes, respectively. Membrane topology of ApST4 is shown with transmembrane (TM) helices 1 – 12 predicted by TMHMM (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM/). Conserved sugar porter family amino acid motifs are highlighted and ApST4 residues that match the motif are coloured red. Predicted ApST4 post-translational modifications include: N-glycosylation (ψ); and phosphorylation at serine (∎) and threonine (▲) residues. (B) Sequence alignment of TM7 of selected GLUT transporters. TM7 from human glucose transporters (GLUTs 1, 3 and 4); human glucose/fructose transporters (GLUTs 2, 5 and 7); and A. pisum glucose/fructose transporters ApST3 (ACYPI004204) and ApST4 (ACYPI001980) are shown. Sequences were aligned using the ClustalX program, and ordered according to their similarity. Boxed regions indicate location of the QLS substrate binding motifs. Asterisks indicate identical residues in all sequences; colon indicates conservative amino acid substitution; dot marks semi-conservative amino acid substitution.
