Fig. 6.
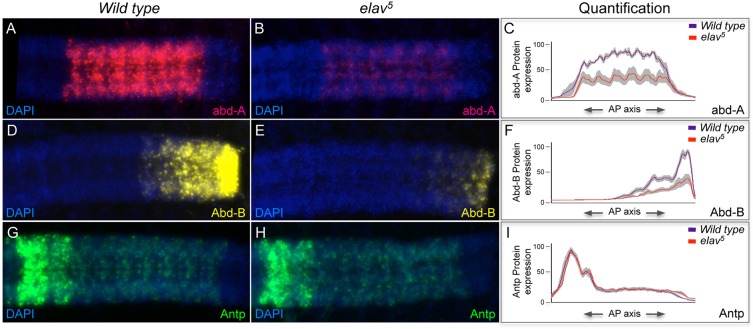
The effects of ELAV removal on the expression of other Hox proteins than Ubx. (A-C) Comparison of expression levels of Abd-A protein in dissected ventral nerve cords of wild type (A) and elav5 mutants (B) reveals that ELAV removal decreases the overall expression of Abd-A protein within the embryonic CNS. (C) Average profile quantification of Abd-A protein along the AP axis of wild-type and elav5 embryos. (D-F) Expression levels of Abd-B protein are much higher in wild-type (D) than in elav5 mutant (E) embryos, revealing that ELAV removal exerts similar effects across all protein-coding genes within the BX-C. (F) Quantification of Abd-B protein expression in wild-type and elav5 mutant embryos. (G-I) The pattern and expression levels of Antp protein are unaffected by ELAV removal. Antp protein expression levels in wild-type embryos (G) are comparable to those in elav5 mutant embryos (H) indicating that the effects of ELAV on Hox protein expression within the CNS vary from gene to gene. (I) Quantification of Antp protein expression in wild-type and elav5 embryos. (C,F,I) Grey shading represents standard error. (A,B,D,E,G,H) DAPI, blue.