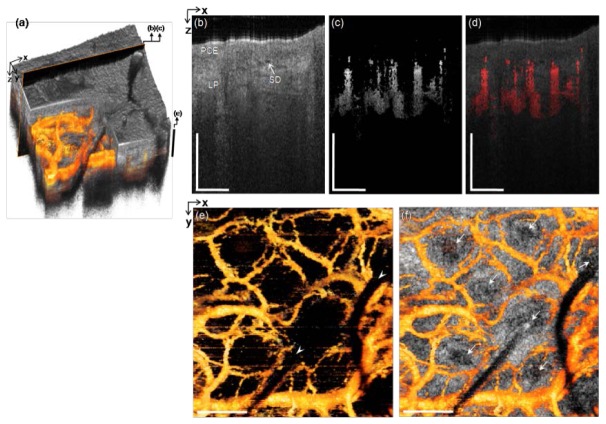
Fig. 8.
In vivo microvascular imaging of inferior turbinate in nasal cavity of a healthy volunteer with the side-viewing probe. (a) 3D rendered OCT structural image with the 3D mOMAG data (yellow) overlay. (b) and (c) Representative cross-sectional structural and mOMAG images (2.0 mm (X) × 1.57 mm (Z)) at a position (a black box) in (a), respectively. (d) Overlay of the mOMAG image (red) on the structural image. PCE: pseudostratified columnar epithelium, LP: lamina propria, SG: seromucinous duct. (e) 2D en face view (2.0 mm (X) × 2.0 mm (Y)) of the 3D mOMAG data volumes taken over depths of 502 µm from the surface, demonstrating vascular characteristics with the ring-like microvasculature. Cut-offs across the vessels (arrow heads) are due to beam shading by the leaned nasal hairs. Black bar in (a) is the depth range for (e). (f) The vasculature with an en face OCT tomogram at 502 µm in depth overlay, indicating that each nasal hair in the hair pores (arrows) is surrounded by ring-like vessels, possibly feeding nutrients for the hair growth. A fly-through image of the microvasculature is shown with a movie clip (Media 5 (5MB, MPG) ). Scale bars: 0.5 mm.