Table 1. Mathematical model of cell identity landscape.
| Landscape Term: Index Notation | Landscape Term: Matrix Notation (dim.) | Biological Interpretation |
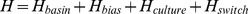
|
Total landscape. | |
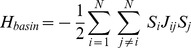
|
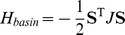
|
Produces cell basins of attraction. |
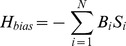
|
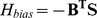
|
External control of individual genes, i.e. inducible expression. |
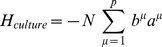
|
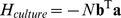
|
External control of specific cell basins, i.e. culturing conditions. |
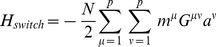
|
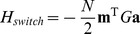
|
Cell switching by signals, i.e. in vivo development. |
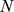
|
Number of TFs, labeled by  , , 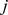 . In this paper N = 1337. . In this paper N = 1337. |
|
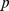
|
Number of cell fates, labeled by 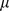 , ,  . In this paper . In this paper 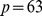 . . |
|
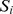
|
 ( (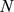 × × ) ) |
State (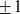 ) of ) of 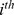 TF. TF. |
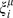
|
 ( (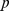 × ×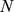 ) ) |
State (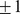 ) of ) of 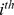 TF in cell fate TF in cell fate 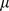 . . |
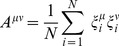
|
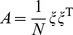 ( ( × × ) ) |
Correlation between cell fate 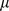 and and  . . |
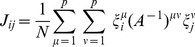
|
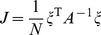 ( (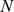 × ×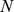 ) ) |
Interaction strength between  and and 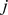 . . |
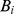
|
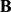 ( (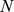 × × ) ) |
External control of 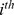 TF. TF. |
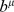
|
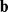 ( (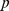 × × ) ) |
External control of 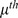 cell fate. cell fate. |
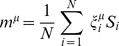
|
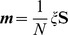 ( (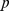 × × ) ) |
Overlap of  on cell fate on cell fate 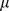 . . |
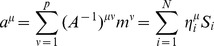
|
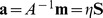 ( (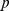 × × ) ) |
Projection of  on cell fate on cell fate 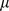 . . |
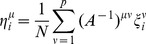
|
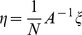 ( (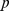 × ×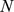 ) ) |
Predictivity of 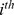 TF in cell fate TF in cell fate 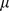 . . |
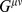
|
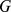 ( (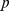 × ×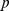 ) ) |
Signal dependent coupling that drives cell fate  to cell fate to cell fate 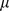
|
This table provides a summary of the landscape model and the biological interpretation of each term. The first column is written in index notation, while the second column is the same term in matrix notation with the dimension of the term given in parenthesis. If no dimension is listed, the term is a single number.
